前言
前一阵子,编译原理课实验内容是要去做一个词法分析器,实现后,觉得没有把正规表达式和NFA、DFA这些知识用上,所以就产生了想自己去实现一个lex的想法,于是就有了这篇博文。
如果还不知道词法分析器该怎么实现,可以去看c语言词法分析初试(C++实现)。
简介
上图是维基百科对lex的定义。
从中可以明确lex的功能:读进一个代表词法分析器规则的输入字符串流,然后输出以C语言实做的词法分析器源代码。
本质上,本人是在对原lex进行模仿,但使用规则细节什么的与其并不一致,比如原lex用正则表达式来表示词法分析器规则,而本人的自制lex使用的是正规表达式,所以接下来关于原lex的内容不再赘述。
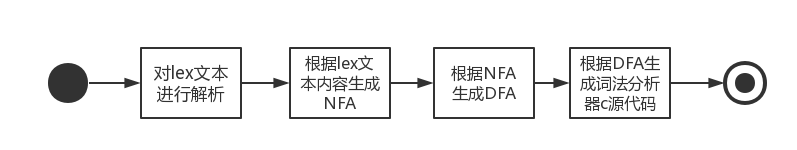
执行流程
1.解析lex文本
1.1文本规则
%{
c代码区块
%}
%!
定义区块
%!
%%
规则1 方法体
%$
规则2 方法体
%$
...
%%
由上可以看到,整个lex文本分为三个区块。
c代码区
用%{ %}包围,里面内容是c代码,这些代码会原样复制进程序生成的词法分析器源代码中,也就是说,我们可以在这个区块里预定义一些c函数、变量等等。
定义区
用%! %!包围,里面内容是一些定义,格式为 a = b。
a表示我们定义一种输入字符,比如所有的字母、数字,或是a-v,3-7等等区间,或是除了字母以外的任何字符。我们可以给这些值的集合起一个名字为a。
b表示一个函数名,该函数接受一个char字符,返回1或者0,表示输入是否匹配。该函数必须自己在c代码区进行实现。
例如:我们定义 digit = isDigit
digit表示所有的数字,则我们需要实现这样一个函数:
int isDigit(char ch){
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
return 1;
return 0;
}
完成上述之后,我们就可以在规则区里以{a}的形式在正规表达式中使用该自定义输入。
规则区
这里可以说是整个lex文件最核心的部分了。
我们需要在这里对所有的词法规则用正规表达式进行描述。
还是举个例子,我们要将c语言的标识符的规则进行描述:
正规表达式 方法体
({letter}|_)({letter}|_|digit)* {printf("<$ID, %s>", LEX_TEXT);}
letter表示所有字母,digit表示所有数字,这两者都属于是我们在定义区所自定义的输入类型。
那么上面正规表达式代表的含义就是所有以字母或者下划线开头并后续字母是字母数字或者下划线的字符串,即是我们认为合法的标识符。
后面{}包含的内容是我们的方法体,即定义我们生成的词法分析器当识别出符合正规式定义的字符串后需要进行的操作,该操作用c语言来进行描述。
LEX_TEXT为我们预设定的保存识别出的串的char数组。
那么上面的规则所定义的就是对标识符进行匹配,并在匹配成功之后将其进行输出。
1.2文本识别细节
这部分做的比较粗略。
1.上述三个区域的界符即%{,%!等必须出现在每行的行首,否则会被忽略。
2.所有出现在三个区域外的文本内容全部忽略
3.当出现文本忽略时会报出警告(文本内容及行号)
4.当出现文本识别错误时会进行报错(文本内容及行号)并程序终止。
5.因为正规式里面原本就有(,),|,*等符号,再加上{}用于标识自定义输入的符号以及空格,这些字符均需要进行转义,我定义的转义标志是%,与c语言的\没有什么区别。用%$表示正规表达式里的空。
根据lex文本内容生成NFA等
这部分我用了一个栈来实现,具体细节可参看之前写的一篇博客正规表达式转NFA(C++),细节有所差异,但是实现思想是一致的,这里就不再重复描述了。
除了要生成NFA,还要完成两件事。
1. 保存定义区里 自定义输入与对应判断函数名的映射。
2. 保存NFA的终点状态的序号集合,并保存其各自对应的方法体的映射。
根据NFA生成DFA
这里使用的方法是子集法:
每个状态表示为一个数字,这一点在上面已经提过,那么我们用一个vector表示一个状态集合。
再使用一个set和一个queue,set用于对vector进行查重,queue用于遍历,从起始状态的集合开始,将其经每个输入到达的状态加入queue,当然,前提是该状态集合没有在set中出现过。
这里有个重点是关于空的处理,见代码。
//i为当前状态,input为输入,state为存放可到达的状态的集合
void Lex::findBeGo(int i, string input, vector<int>* state)
{
for(auto x : nfaVet[i])
{
int sId = x.toId;
bool flag = true;
for(auto iter=state->begin(); iter!=state->end(); iter++)
if((*iter) == sId)
{
flag = false;
break;
}
if(flag && input.compare(x.input) == 0)
{
state->push_back(sId);
findBeGo(sId, "", state);
}
}
}当然,这里也需要保存DFA的终点状态的序号,并保存其各自对应的方法体的映射。
将DFA转换为C代码
如果用自动机的模式写过一次词法分析器,就很明了,DFA只跟自动机的状态里面内容相关。
即:switch(状态){//} ;里面的内容是需要根据DFA动态生成的,其他的都不需要改变。
所以我们一开始就将switch部分上下的代码都确定,然后根据DFA来生成。
对每一个case来说,我们需要输出的内容只有以下几点:
1. 状态id
2. 状态接受的输入,以及该输入转向的状态id
3. 枚举完所有可接受的输入后,如果当前字符与以上输入都不符合,那么根据该状态是否是终止状态来确定是结束并执行方法体还是报错。 例子如下:
case ID:
{
ch = *str++;
SYLEX_TEXT[SYLEX_TEXT_LEN++]=ch;
if(ch == 输入1){
SYLEX_STATE = 转向的状态;
}
else
if(ch == 输入2){
SYLEX_STATE = 转向的状态;
}
else
{
//根据id是否可终止,来决定是报错还是执行方法体
}这里还有个细节,关于我们的自定义输入,因为普通输入字符我们直接是用if(ch == ‘X’)来判断。而自定义输入,我们是通过if(函数名(ch))来判断,所以在输出源代码时,需要先对其输入进行判断是否是自定义输入,这里我们用第一步时建立的映射直接就可以解决。
源码
全部流程都封装在了Lex类中,因为篇幅问题,就只贴类的成员变量和成员函数声明部分的代码。
有兴趣的朋友,可以去github上看完整代码,链接如下。
shiyi1996/project/tree/master/Lex
//
// Lex.hpp
// Lex
//
// Created by shiyi on 2016/10/18.
// Copyright © 2016年 shiyi. All rights reserved.
//
#ifndef Lex_hpp
#define Lex_hpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
Node(int fromId, string input, int toId)
{
this->fromId = fromId;
this->input = input;
this->toId = toId;
}
int fromId;
string input;
int toId;
};
class Lex
{
public:
static const int MAXID = 100000;
Lex(string _lexFile);
Lex(string _lexFile, string _outCFile);
void init();
//写入scanner函数之前
void outCodeLeft();
//写入scanner函数之后
void outCodeRight();
//写入scanner函数
void outCodeMid();
//解析lex源文件
void scanner();
//错误警告等输出
inline void printError(int line, string str, string mess);
inline void printWaring(int line, string str, string mess);
//解析方法体
void getFunc(string str, int line);
//解析正规式
void getRegular(string str, int line);
//------日后补充
//判断正规式是否合法
bool isExpre(vector<pair<string, bool>>);
//DFA最小化
void getSimpDFA();
// -----------
//添加NFA节点
inline void addNFANode(int fromId, string input, int toId);
//添加DFA节点
inline void addDFANode(int fromId, string input, int toId);
//正规式转NFA
void regrToNFA(vector<pair<string, bool>> regr, int startId, int endId, int &itemId);
//生成NFA
void getNFA();
//生成DFA
void getDFA();
//nfa查询
void findBeGo(int i, string input, vector<int>* state);
//获取nfa目标状态集合
vector<int>* getState(vector<int>* fromState, string input);
//获取终态
void getVt(map<vector<int>, int> stateMap);
//执行操作
void work();
//输出-测试-
inline void print();
private:
string lexFile;
string outCFile;
//自定义输入对应方法体
map<string, string> funcMap;
//正规式
vector<vector<pair<string, bool>>> regrVet;
//方法体
vector<string> funcVet;
//NFA
vector<Node> nfaVet[MAXID];
//DFA
vector<Node> dfaVet[MAXID];
//储存所有输入
set<string> inputSet;
//DFAend
int dfaEnd[MAXID];
//NFAend 值为funcVet item的下标
int nfaEnd[MAXID];
int nfaNum;
int dfaNum;
};
#endif /* Lex_hpp */测试
Lex代码
%{
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
const int KEY_NUM = 32;
const char* KEY_SET[] = {
"auto", "break", "case", "char", "const", "continue",
"default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extern",
"float", "for", "goto", "if", "int", "long", "register",
"return", "short", "signed", "sizeof", "static", "struct",
"switch", "typedef", "union", "unsigned", "void", "volatile",
"while"
};
int isDigit(char ch)
{
if(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0')
return 1;
return 0;
}
int isLetter(char ch)
{
if((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'))
return 1;
return 0;
}
int getKeyId(char *str)
{
for(int i=0; i<KEY_NUM; i++)
{
if(strcmp(KEY_SET[i], str) == 0)
return i+1;
}
return 0;
}
int isNoOne(char ch)
{
if(ch != '\'' && ch != '\0')
return 1;
return 0;
}
int isNoTow(char ch)
{
if(ch != '\"' && ch != '\0')
return 1;
return 0;
}
%}
%!
noone=isNoOne
notow=isNoTow
letter=isLetter
digit=isDigit
%!
%%
({letter}|_)({letter}|_|{digit})* {
int id = getKeyId(SYLEX_TEXT);
if(id != 0)
printf("<%s,->\n", SYLEX_TEXT);
else
{
printf("<$ID,%s>\n", SYLEX_TEXT);
}
}
%$
(+|-|%$){digit}{digit}*(.{digit}{digit}*|%$)((E|e){digit}{digit}*|%$) {
printf("<$NUM,%s>\n", SYLEX_TEXT);
}
%$
%(|%)|%{|%}|[|]|;|,|. {
printf("<%s,->\n", SYLEX_TEXT);
}
%$
% |{\t}|{\n} {
}
%$
(%*(%=|%$))|(/(=|%$))|(+(+|=|%$))|(-(-|=|%$))|(<(<|=|%$))|(>(>|=|%$))|(=(=|%$))|(&(&|=|%$))|(%|(%||=|%$))|(^(=|%$))|(~(=|%$)) {
printf("<%s,->\n", SYLEX_TEXT);
}
%$
({\'}{noone}*{\'})|({\"}{notow}*{\"}) {
printf("<$STR,%s>\n", SYLEX_TEXT);
}
%$
#include(% )*((<({letter}|_)({letter}|_|{digit})*.h>)|("({letter}|_)({letter}|_|{digit})*.h")) {
printf("%s 应该预处理的,暂时先忽略", SYLEX_TEXT);
}
%%生成的词法分析器C代码
//%{ start
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
const int KEY_NUM = 32;
const char* KEY_SET[] = {
"auto", "break", "case", "char", "const", "continue",
"default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extern",
"float", "for", "goto", "if", "int", "long", "register",
"return", "short", "signed", "sizeof", "static", "struct",
"switch", "typedef", "union", "unsigned", "void", "volatile",
"while"
};
int isDigit(char ch)
{
if(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0')
return 1;
return 0;
}
int isLetter(char ch)
{
if((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'))
return 1;
return 0;
}
int getKeyId(char *str)
{
for(int i=0; i<KEY_NUM; i++)
{
if(strcmp(KEY_SET[i], str) == 0)
return i+1;
}
return 0;
}
int isNoOne(char ch)
{
if(ch != '\'' && ch != '\0')
return 1;
return 0;
}
int isNoTow(char ch)
{
if(ch != '\"' && ch != '\0')
return 1;
return 0;
}
//%} end
//%! start
//%! end
//%% start
//%% end
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SYLEX_MAXSIZE_TEXT 120
#define SYLEX_MAXSIZE_BUFF 1024
char SYLEX_FILE_NAME[100];
char SYLEX_OUT_FILE_NAME[100];
int SYLEX_LINE = 0;
int SYLEX_STATE = 0;
int SYLEX_TEXT_LEN = 0;
char SYLEX_TEXT[SYLEX_MAXSIZE_TEXT];
char SYLEX_BUFF[SYLEX_MAXSIZE_BUFF];
//扫描函数
void SYLEX_scanner(char *str)
{
char ch = ' ';
while(ch != '\0')
{
//printf("%c %d\n", ch, SYLEX_STATE);
switch(SYLEX_STATE) {
case 0:
{
ch = *str++;
SYLEX_TEXT[SYLEX_TEXT_LEN++]=ch;
if(ch == ' '){
SYLEX_STATE = 1;
}
else
if(ch == '#'){
SYLEX_STATE = 2;
}
else
if(ch == '&'){
SYLEX_STATE = 3;
}
else
if(ch == '('){
SYLEX_STATE = 4;
}
else
//。。。
else
if(ch == '}'){
SYLEX_STATE = 28;
}
else
if(ch == '~'){
SYLEX_STATE = 29;
}
else
{
printf("Error in line %d\n", SYLEX_LINE);
exit(1);
}
break;
}
case 1:
{
ch = *str++;
SYLEX_TEXT[SYLEX_TEXT_LEN++]=ch;
{
SYLEX_TEXT[SYLEX_TEXT_LEN-1] = '\0';
SYLEX_TEXT_LEN=0;
SYLEX_STATE=0;
str--;
//**************s
{}
//**************e
}
break;
}
//考虑篇幅,省略中间的状态
case 81:
{
ch = *str++;
SYLEX_TEXT[SYLEX_TEXT_LEN++]=ch;
{
SYLEX_TEXT[SYLEX_TEXT_LEN-1] = '\0';
SYLEX_TEXT_LEN=0;
SYLEX_STATE=0;
str--;
//**************s
{ printf("%s 应该预处理的,暂时先忽略", SYLEX_TEXT);}
//**************e
}
break;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **args)
{
if(argc == 1)
{
printf("没有输入源文件名");
return 0;
}
else if(argc == 2)
{
strcpy(SYLEX_FILE_NAME, args[1]);
sprintf(SYLEX_OUT_FILE_NAME, "%s.out", SYLEX_FILE_NAME);
}
else
{
strcpy(SYLEX_FILE_NAME, args[1]);
strcpy(SYLEX_OUT_FILE_NAME, args[2]);
}
FILE* file = fopen(SYLEX_FILE_NAME, "r");
while(NULL != fgets(SYLEX_BUFF, SYLEX_MAXSIZE_BUFF, file))
{
++SYLEX_LINE;
SYLEX_scanner(SYLEX_BUFF);
}
return 0;
}测试C代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include"aaa.h"
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int b = a + 3.5E3;
char s[] = "I love the world\n";
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
printf("%s\n",s);
}输出
#include <stdio.h> 应该预处理的,暂时先忽略#include <string.h> 应该预处理的,暂时先忽略#include"aaa.h" 应该预处理的,暂时先忽略<int,->
<$ID,main>
<(,->
<),->
<{,->
<int,->
<$ID,a>
<=,->
<$NUM,5>
<;,->
<int,->
<$ID,b>
<=,->
<$ID,a>
<+,->
<$NUM,3.5E3>
<;,->
<char,->
<$ID,s>
<[,->
<],->
<=,->
<$STR,"I love the world\n">
<;,->
<for,->
<(,->
<int,->
<$ID,i>
<=,->
<$NUM,0>
<;,->
<$ID,i>
<<,->
<$NUM,5>
<;,->
<$ID,i>
<++,->
<),->
<$ID,printf>
<(,->
<$STR,"%s\n">
<,,->
<$ID,s>
<),->
<;,->
<},->