源码版本:4.0.1
源码位置:
1. 整数集合简介
intset是Redis内存数据结构之一,和之前的 sds、 skiplist、dict、adlist 等通用数据相比,它是Redis特有的,用来实现Redis的Set结构(当元素较小且为数字类型时),它的特点有:
- 元素类型只能为数字。
- 元素有三种类型:int16_t、int32_t、int64_t。
- 元素有序,不可重复。
- intset和sds一样,内存连续,就像数组一样。
2. 数据结构定义
typedef struct intset {
uint32_t encoding; // 编码类型 int16_t、int32_t、int64_t
uint32_t length; // 长度 最大长度:2^32
int8_t contents[]; // 柔性数组
} intset;3. 创建、插入(扩缩容)、查找(二分查找)、删除
以下面这个例子来看下intset的各种操作:
(需要自己在server.c中添加intset.h头文件,然后将main函数修改成下面代码)
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
uint8_t ret;
uint8_t success;
int64_t value;
int16_t int16_a = 2 * 128;
int16_t int16_b = 2 * 256;
int32_t int32_c = 2 * 65536;
printf("----------intset insert----------\n");
intset *is = intsetNew();
is = intsetAdd(is, int16_a, &success);
if (success == 0) {
printf("add int16_a fail\n");
} else {
printf("add int16_a success, ");
}
printf("is encoding:%d, length:%d, bloblen:%zu\n", is->encoding, intsetLen(is), intsetBlobLen(is));
is = intsetAdd(is, int32_c, &success);
if (success == 0) {
printf("add int32_c fail\n");
} else {
printf("add int32_c success, ");
}
printf("is encoding:%d, length:%d, bloblen:%zu\n", is->encoding, intsetLen(is), intsetBlobLen(is));
is = intsetAdd(is, int16_b, &success);
if (success == 0) {
printf("add int16_b fail\n");
} else {
printf("add int16_b success, ");
}
printf("is encoding:%d, length:%d, bloblen:%zu\n", is->encoding, intsetLen(is), intsetBlobLen(is));
printf("----------intset found----------\n");
ret = intsetFind(is, int16_b);
if (ret == 1) {
printf("int16_b is found\n");
}
printf("----------intset get----------\n");
ret = intsetGet(is, 0, &value);
if (ret != 0) {
printf("int16_a get value is %lld\n", value);
}
printf("----------intset remove----------\n");
is = intsetRemove(is, int16_b, &success);
if (success == 1) {
printf("int16_b is success remove\n");
}
printf("is encoding:%d, length:%d, bloblen:%zu\n", is->encoding, intsetLen(is), intsetBlobLen(is));
zfree(is);
return 0;
}
Out >
----------intset insert----------
add int16_a success, is encoding:2, length:1, bloblen:10
add int32_c success, is encoding:4, length:2, bloblen:16
add int16_b success, is encoding:4, length:3, bloblen:20
----------intset found----------
int16_b is found
----------intset get----------
int16_a get value is 256
----------intset remove----------
int16_b is success remove
is encoding:4, length:2, bloblen:163.1 创建
intset *is = intsetNew(),创建了一个空的名为is的intset,代码如下:
/* Create an empty intset. */
intset *intsetNew(void) {
intset *is = zmalloc(sizeof(intset)); // 分配空间
is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(INTSET_ENC_INT16); // 初试创建默认元素大小为 2 字节
is->length = 0;
return is;
}3.2 插入
- 接下来我们调用
intsetAdd()连续插入了三次数据,它的代码如下:
/* Insert an integer in the intset */
intset *intsetAdd(intset *is, int64_t value, uint8_t *success) {
uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);
uint32_t pos;
if (success) *success = 1;
/* Upgrade encoding if necessary. If we need to upgrade, we know that
* this value should be either appended (if > 0) or prepended (if < 0),
* because it lies outside the range of existing values. */
if (valenc > intrev32ifbe(is->encoding)) {
/* This always succeeds, so we don't need to curry *success. */
return intsetUpgradeAndAdd(is,value);
} else {
/* Abort if the value is already present in the set.
* This call will populate "pos" with the right position to insert
* the value when it cannot be found. */
if (intsetSearch(is,value,&pos)) {
if (success) *success = 0;
return is;
}
is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
if (pos < intrev32ifbe(is->length)) intsetMoveTail(is,pos,pos+1);
}
_intsetSet(is,pos,value);
is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
return is;
}整个函数的流程如下:
uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value),根据value的长度获取其对应的编码,保存至valenc。if (valenc > intrev32ifbe(is->encoding)),如果valenc > is->encoding,表明目前的encoding太小,需要整体提高encoding的大小。
- 执行intsetUpgradeAndAdd()完成扩大操作。
- 如果valenc <= is->encoding。
- 执行查找
intsetSearch(is,value,&pos),如果查找到元素,将success置为0,表示插入失败,即此元素已经存在。 - 如果没有查找到,pos表示元素应该插入的位置,则给is扩容一个元素的大小
intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1),如果需要则使用intsetMoveTail(is,pos,pos+1)将元素挪移。
- 执行查找
_intsetSet(is,pos,value),将元素插入intset。is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1),更新length的值。
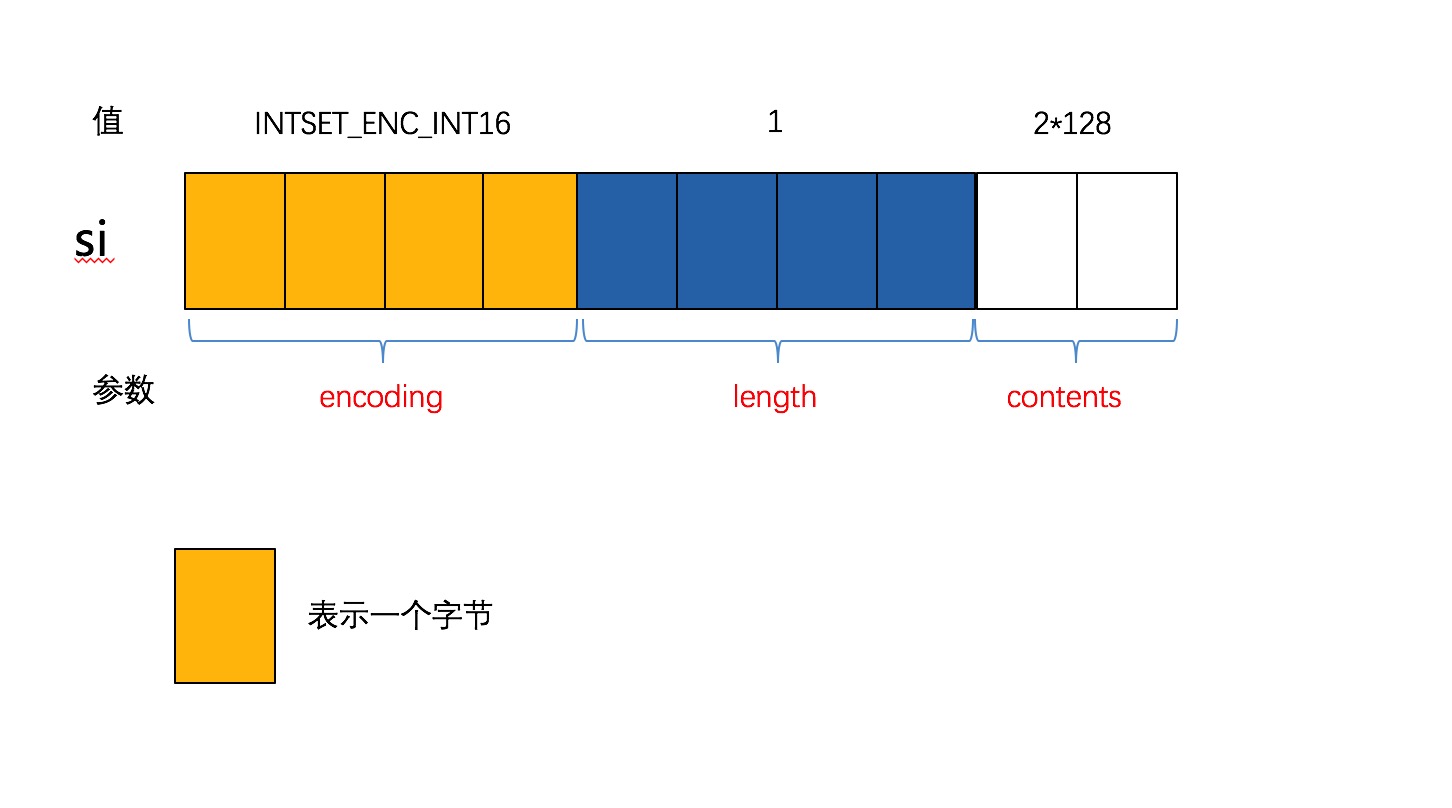
插入了第一个元素int16_a的is如下图所示:
与输出结果相对应:
add int16_a success, is encoding:2, length:1, bloblen:10- 接下来我们的代码添加了第二个元素,由于它的大小超过了
INTSET_ENC_INT16,所以添加操作会执行intsetUpgradeAndAdd()函数扩大encoding:
/* Upgrades the intset to a larger encoding and inserts the given integer. */
static intset *intsetUpgradeAndAdd(intset *is, int64_t value) {
uint8_t curenc = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);
uint8_t newenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);
int length = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
int prepend = value < 0 ? 1 : 0;
/* First set new encoding and resize */
is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(newenc);
is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
/* Upgrade back-to-front so we don't overwrite values.
* Note that the "prepend" variable is used to make sure we have an empty
* space at either the beginning or the end of the intset. */
while(length--)
_intsetSet(is,length+prepend,_intsetGetEncoded(is,length,curenc));
/* Set the value at the beginning or the end. */
if (prepend)
_intsetSet(is,0,value);
else
_intsetSet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length),value);
is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
return is;
}- 将is目前的encoding保存至curenc,将value的encoding保存至newenc。
int prepend = value < 0 ? 1 : 0,prepend用来确定新value的插入位置:第一个还是最后一个,因为它的encoding比is->encoding要大,所以它要么比目前所有元素都大,要么比所有元素都小,即插入位置要么第一个,要么最后一个。- 然后更新encoding的值,重新分配空间。
- 挪动所有的元素到新位置。
- 根据prepend的值判断将value插入第一个位置还是最后一个位置。
- 更新is->length。
有一个比较生动的图解如下,参考[1]:
/* Upgrade back-to-front so we don't overwrite values.
* Note that the "prepend" variable is used to make sure we have an empty
* space at either the beginning or the end of the intset. */
// 根据集合原来的编码方式,从底层数组中取出集合元素
// 然后再将元素以新编码的方式添加到集合中
// 当完成了这个步骤之后,集合中所有原有的元素就完成了从旧编码到新编码的转换
// 因为新分配的空间都放在数组的后端,所以程序先从后端向前端移动元素
// 举个例子,假设原来有 curenc 编码的三个元素,它们在数组中排列如下:
// | x | y | z |
// 当程序对数组进行重分配之后,数组就被扩容了(符号 ? 表示未使用的内存):
// | x | y | z | ? | ? | ? |
// 这时程序从数组后端开始,重新插入元素:
// | x | y | z | ? | z | ? |
// | x | y | y | z | ? |
// | x | y | z | ? |
// 最后,程序可以将新元素添加到最后 ? 号标示的位置中:
// | x | y | z | new |
// 上面演示的是新元素比原来的所有元素都大的情况,也即是 prepend == 0
// 当新元素比原来的所有元素都小时(prepend == 1),调整的过程如下:
// | x | y | z | ? | ? | ? |
// | x | y | z | ? | ? | z |
// | x | y | z | ? | y | z |
// | x | y | x | y | z |
// 当添加新值时,原本的 | x | y | 的数据将被新值代替
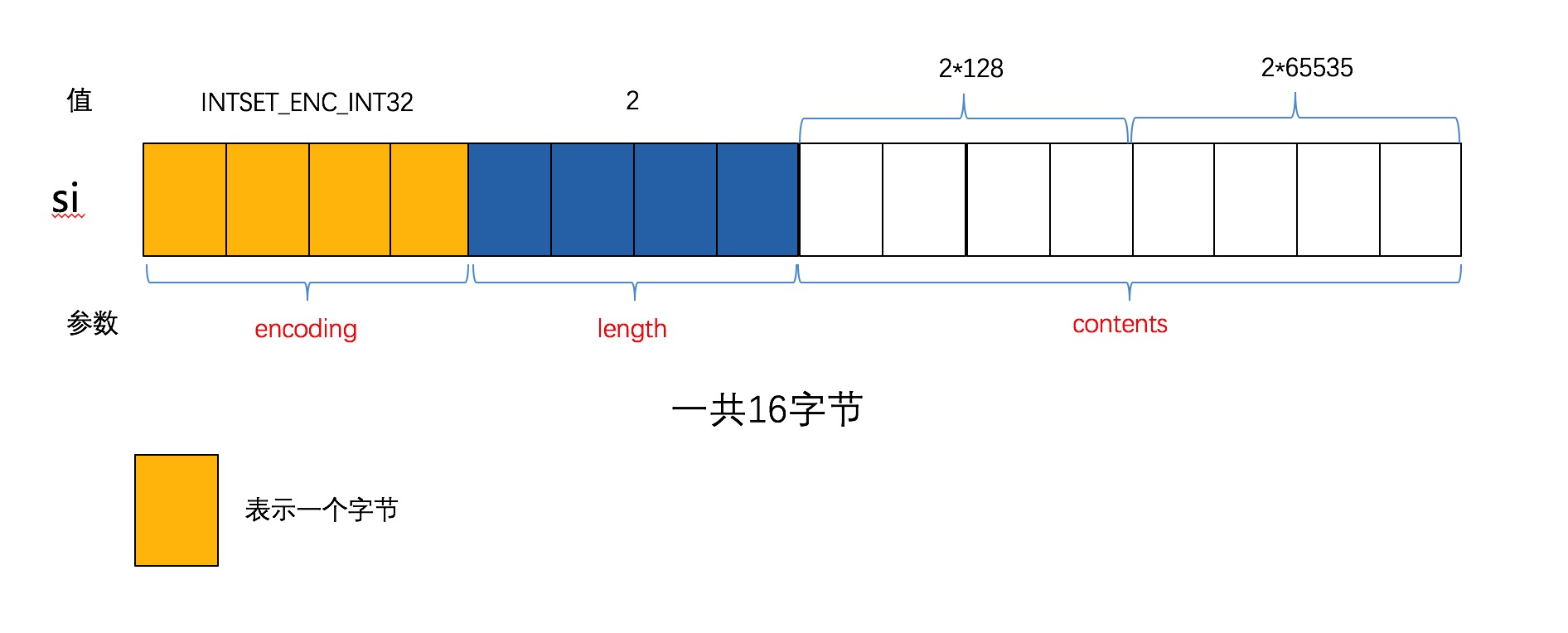
// | new | x | y | z |插入了第二个元素之后is如下图所示:
输出如下所示:
add int32_c success, is encoding:4, length:2, bloblen:16- 接下来我们插入第三个元素,此时的encoding满足
int16_b的大小,所以代码分支去执行查找操作intsetSearch()函数:
/* Search for the position of "value". Return 1 when the value was found and
* sets "pos" to the position of the value within the intset. Return 0 when
* the value is not present in the intset and sets "pos" to the position
* where "value" can be inserted. */
static uint8_t intsetSearch(intset *is, int64_t value, uint32_t *pos) {
int min = 0, max = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1, mid = -1;
int64_t cur = -1;
/* The value can never be found when the set is empty */
if (intrev32ifbe(is->length) == 0) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
} else {
/* Check for the case where we know we cannot find the value,
* but do know the insert position. */
if (value > _intsetGet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1)) {
if (pos) *pos = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
return 0;
} else if (value < _intsetGet(is,0)) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
}
}
while(max >= min) {
mid = ((unsigned int)min + (unsigned int)max) >> 1; // 加法运算级别比移位高
cur = _intsetGet(is,mid);
if (value > cur) {
min = mid+1;
} else if (value < cur) {
max = mid-1;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (value == cur) {
if (pos) *pos = mid;
return 1;
} else {
if (pos) *pos = min;
return 0;
}
}- 如果目前is->length为0,则标记pos为0,并且返回查找失败。
- 如果value比最大值还大,或者比最小值还小,标记pos为length或者0,返回查找失败。
- 否则使用二分法查找到元素,将pos指向应当插入的位置。
等到intsetSearch()返回之后,pos表示value应当插入的位置,此时需要挪动pos之后的元素向后一个位置,挪动函数是intsetMoveTail():
static void intsetMoveTail(intset *is, uint32_t from, uint32_t to) {
void *src, *dst;
uint32_t bytes = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-from;
uint32_t encoding = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);
if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT64) {
src = (int64_t*)is->contents+from;
dst = (int64_t*)is->contents+to;
bytes *= sizeof(int64_t);
} else if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT32) {
src = (int32_t*)is->contents+from;
dst = (int32_t*)is->contents+to;
bytes *= sizeof(int32_t);
} else {
src = (int16_t*)is->contents+from;
dst = (int16_t*)is->contents+to;
bytes *= sizeof(int16_t);
}
memmove(dst,src,bytes);
}实际上是把内存整体向后移动了一个元素的位置,需要注意的是 memmove 函数允许src和dst之间的内存有重叠部分。
再来一段生动的图解,同样出自参考[1]:
/*
* 向前或先后移动指定索引范围内的数组元素
*
* 函数名中的 MoveTail 其实是一个有误导性的名字,
* 这个函数可以向前或向后移动元素,
* 而不仅仅是向后
*
* 在添加新元素到数组时,就需要进行向后移动,
* 如果数组表示如下(?表示一个未设置新值的空间):
* | x | y | z | ? |
* |<----->|
* 而新元素 n 的 pos 为 1 ,那么数组将移动 y 和 z 两个元素
* | x | y | y | z |
* |<----->|
* 接着就可以将新元素 n 设置到 pos 上了:
* | x | n | y | z |
*
* 当从数组中删除元素时,就需要进行向前移动,
* 如果数组表示如下,并且 b 为要删除的目标:
* | a | b | c | d |
* |<----->|
* 那么程序就会移动 b 后的所有元素向前一个元素的位置,
* 从而覆盖 b 的数据:
* | a | c | d | d |
* |<----->|
* 最后,程序再从数组末尾删除一个元素的空间:
* | a | c | d |
* 这样就完成了删除操作。
*
* T = O(N)
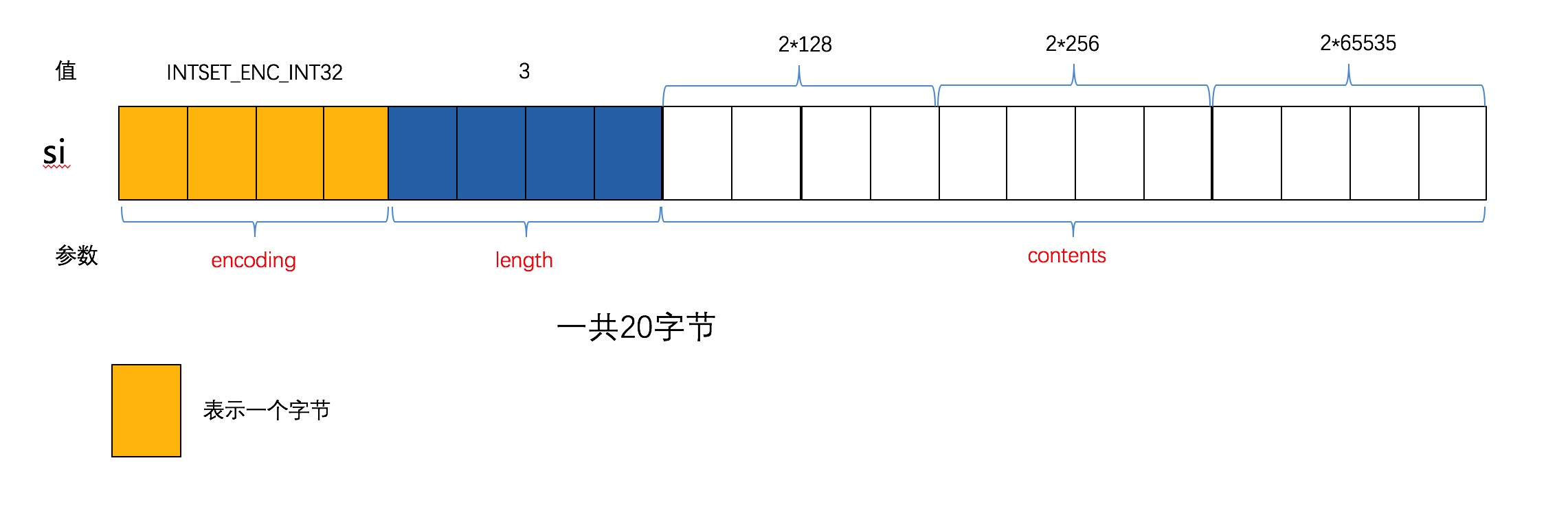
*/此时的is如下图所示:
3.3 查找
查找的逻辑在上面插入操作时候已经说到了,实际上是二分查找。
3.4 删除
/* Delete integer from intset */
intset *intsetRemove(intset *is, int64_t value, int *success) {
uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);
uint32_t pos;
if (success) *success = 0;
if (valenc <= intrev32ifbe(is->encoding) && intsetSearch(is,value,&pos)) {
uint32_t len = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
/* We know we can delete */
if (success) *success = 1;
/* Overwrite value with tail and update length */
if (pos < (len-1)) intsetMoveTail(is,pos+1,pos);
is = intsetResize(is,len-1);
is->length = intrev32ifbe(len-1);
}
return is;
}
- 首先获取元素的encoding,如果不符合条件,success为0表示删除失败。
- 否则调用
intsetSearch()查找到相应的位置 - 然后将
pos+1的元素移动到pos位置上,相当于向前覆盖一个元素。 - 将元素个数减一,重新分配内存。
4. 总结
本篇博客分析了intset的数据结构以及基本操作,整个数据结构还是比较简单的。
个人觉得intset实现按照元素不断增大可以扩大encoding对内存非常友好,但是它没有提供对应的减小encoding操作,即可以一直扩大encoding编码类型,但是不能缩小,这一点不太好。
参考资料:
[1] Redis源码注释3.0-黄健宏
[完]