一、文件的输入输出
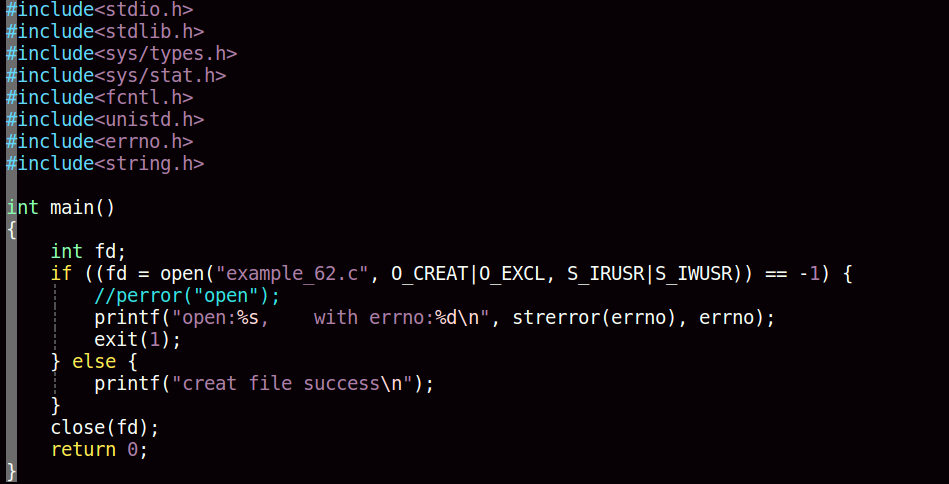
open
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);成功调用返回一个文件描述符,错误返回-1
参数
pathname:要打开或创建的含路径的文件名
flags:打开文件的方式

mode:当且仅当第二个参数使用了O_CREAT时,需使用第三个参数以说明新文件的存取权限。
creat
#include<sys/types.h>
#iclude<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int creat(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);成功调用返回一个文件描述符,错误返回-1
参数
pathname:要打开或创建的文件名,如果pathname指向的文件不存在,则创建一个新文件,如果存在,则原文件将被新文件覆盖。
mode:文件权限。
close
#include<unistd.h>
int close(int fd);成功调用返回0,错误返回-1。
参数
fd:需要关闭的文件的描述符,由open或creat函数得到。
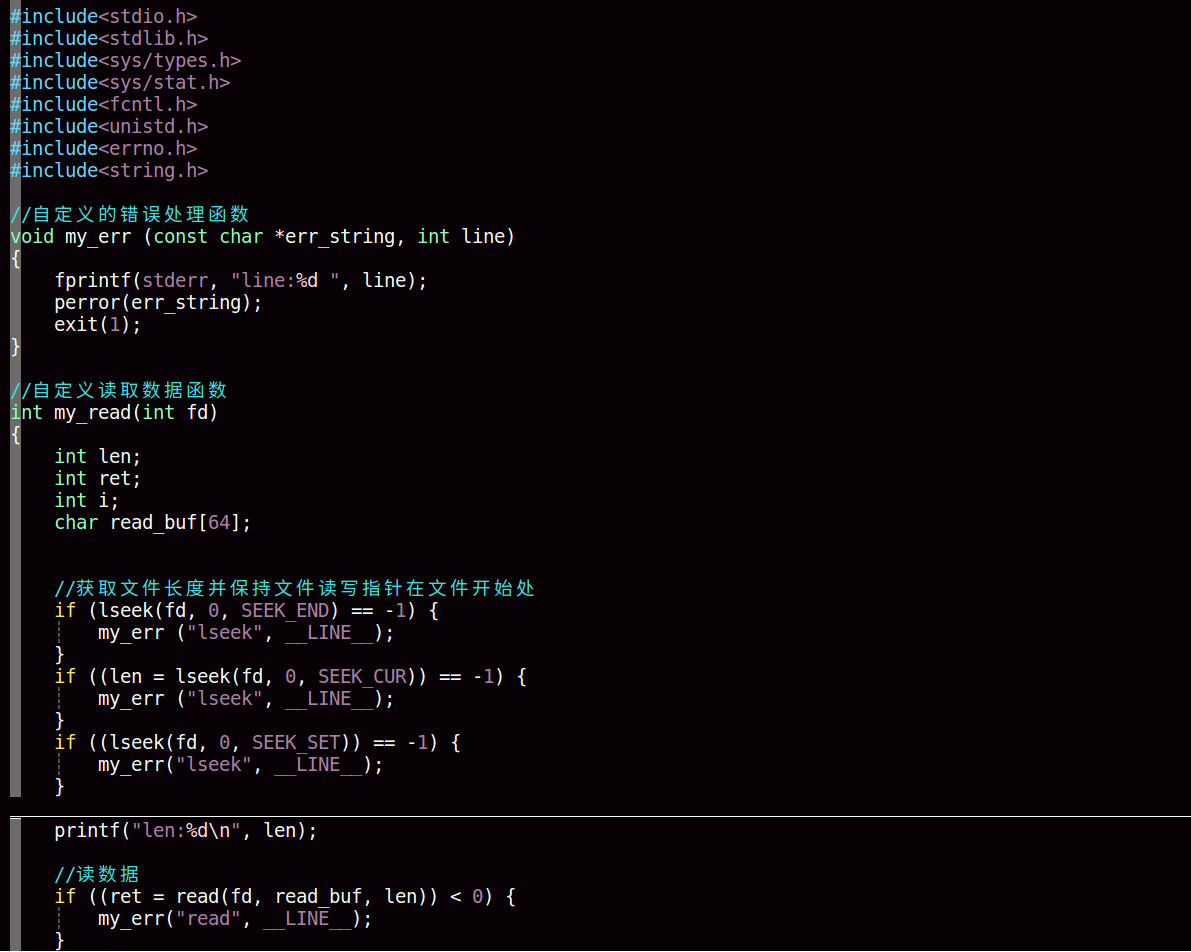
利用open或creat系统调用创建一个新文件
二、文件的读写
read
#include<unistd.h>
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);返回值表示实际读取到的字节,返回0,表示已达文件尾或无可读取的数据,错误返回-1
参数
从文件描述符fd所指向的的文件中读取count个字节的数据到buf所指向的缓存中
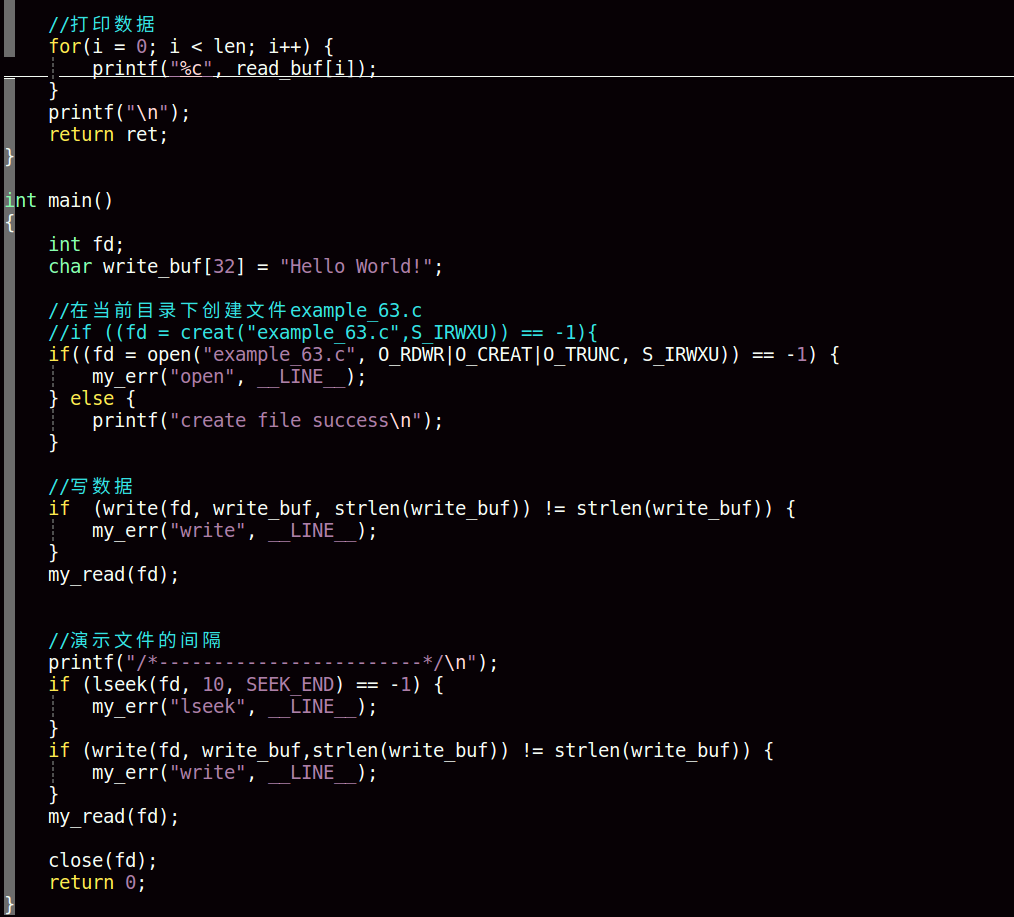
write
#include<unistd.h>
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count)成功调用返回写入字节数,错误返回-1
参数
将buf所指向的缓冲区中的count个字节数据写入到由文件描述符fd所指示的文件中
三、文件读写指针的移植
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
off_t lseek(int fildes, off_t offset, int whence);成功调用返回当前读写位置,错误返回-1
参数
fildes:已打开的文件描述符
offset:根据参数whence来移动读写位置的位移数
whence:开始位置
文件读写和文件读写指针的移动操作过程