关于cjson的介绍和使用方法就不在这里介绍了,详情请查看上一篇博客cjson使用方法。
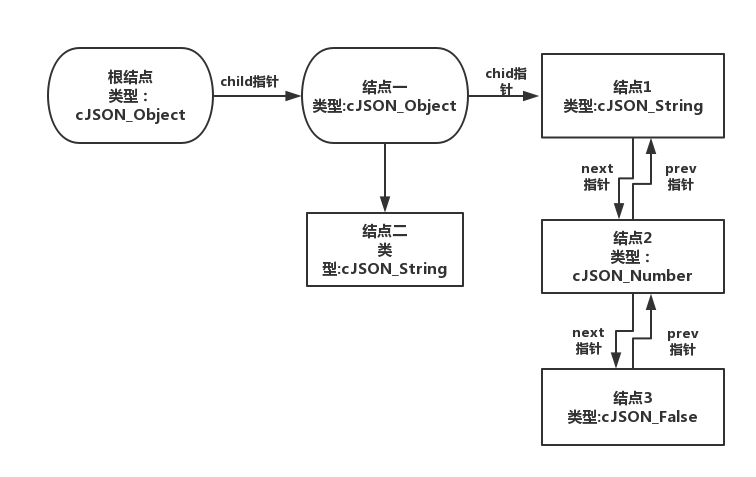
JSON的内存结构像广义表,可以认为是有层次的双向链表。
cJSON程序中的细节点如下:
- 大量宏替换
- 大量静态函数
- 错误处理机制
- 字符串处理时存在utf16转utf9,编码转换
- 用函数指针封装malloc,free,方便用于处理,比如在申请后初始化,或者释放前进行一些处理等。
cJSON中的重要接口函数如下:
解析函数
cJSON * cJSON_Parse(const char *value);
打印函数
char * cJSON_Print(cJSON * item);
删除函数
void cJSON_Delete(cJSON * c);
构造函数
create系列和add系列
解析字符串
char *parse_string(cJSON*item,const char *str)
解析数字
char *parse_number(cJSON *item,const char *num)
解析数组
char *parse_array(cJSON *item,const char *value)
解析对象
char *parse_object(cJSON *item,const char *value)
......cjosn有两个相关的文件,一个cJSON.c和cJSON.h。我们先从头文件开始分析。
首先,我们会看到头文件的开头和结尾这样的语句:
#ifndef cJSON__h
#define cJSON__h
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif...
...
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif#ifndef cJSON_h,#define cJSON_h,#endif . 这是为了防止头文件被重复引用。
extern "C"的主要作用就是为了能够正确实现C++代码调用其他C语言代码。加上extern "C"后,会指示编译器这部分代码按C语言的进行编译,而不是C++的。由于C++支持函数重载,因此编译器编译函数的过程中会将函数的参数类型也加到编译后的代码中,而不仅仅是函数名;而C语言并不支持函数重载,因此编译C语言代码的函数时不会带上函数的参数类型,一般之包括函数名。
接着往下看,就会看到cjson的结构体的定义,cjson对象存储结构实际是一个结构体。
// JSON的一个value的结构体
typedef struct cJSON
{
struct cJSON *next,*prev; // 同一级的元素使用双向列表存储
struct cJSON *child; // 如果是一个object或array的话,child为第一个儿子的指针
int type; // value的类型
char *valuestring; // 如果这个value是字符串类型,则此处为字符串值
int valueint; // 如果是数字的话,整数值
double valuedouble; // 如果是数字的话,读点数值
char *string; // json对象的名称
} cJSON;
前面提到过,cjson的存储结构像一个广义表,其实也可以说是一个树,不过兄弟结点之间都通过prev和next两个指针连接起来。
prev和next分别是cjson对象的前驱和后继,属于同一级别的对象。chid则指向孩子结点,并且是第一个孩子的指针。
示例图如下:
cjson的类型宏定义:
/* cJSON Types: */
#define cJSON_False (1 << 0)
#define cJSON_True (1 << 1)
#define cJSON_NULL (1 << 2)
#define cJSON_Number (1 << 3)
#define cJSON_String (1 << 4)
#define cJSON_Array (1 << 5)
#define cJSON_Object (1 << 6)
#define cJSON_IsReference 256
#define cJSON_StringIsConst 512这些宏定义是对结构体type的值定义,处理时只需要将type的值&255进行位运算,即可得到json里储存的数据类型。
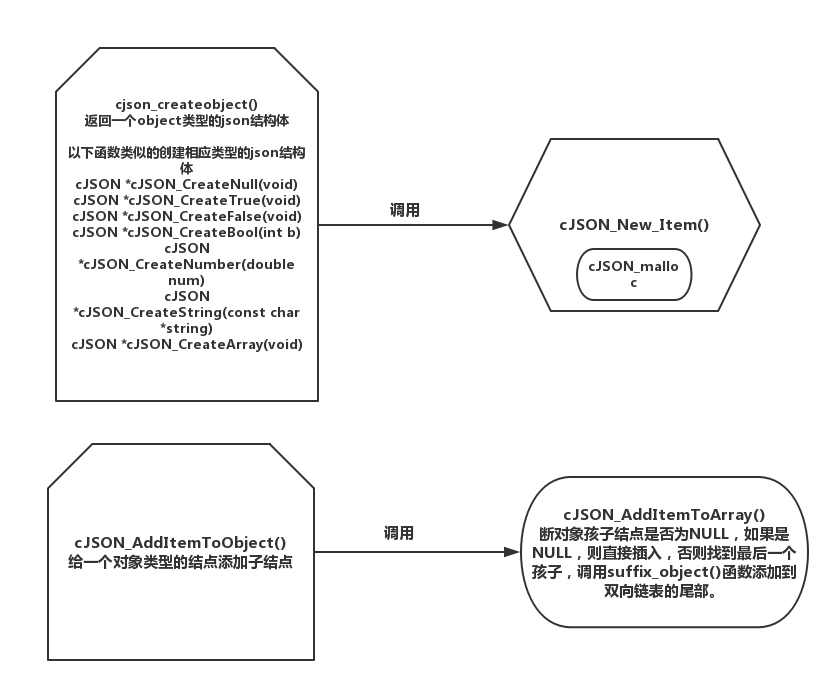
cjson的创建的过程就是创建一个cjson结构体,再通过add一系列函数将其他孩子结点数据或同等级结点加入,将相关结点通过指针链起来。
cjson_create一系列函数:cJSON_CreateArray(),cJSON_CreateObject(),cJSON_CreateString()等函数,都是调用cJSON_New_Item()函数创建对应节点信息。函数返回一个json结构体指针。
相关函数如下:
static cJSON *cJSON_New_Item(void) //创建json结构体
{
cJSON *node = (cJSON *) cJSON_malloc(sizeof(cJSON));
if (node)
memset(node, 0, sizeof(cJSON)); //初始化结构体
return node;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = cJSON_NULL;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateTrue(void)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = cJSON_True;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateFalse(void)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = cJSON_False;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateBool(int b)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = b ? cJSON_True : cJSON_False;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateNumber(double num)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item) {
item->type = cJSON_Number;
item->valuedouble = num;
item->valueint = (int) num;
}
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateString(const char *string)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item) {
item->type = cJSON_String;
item->valuestring = cJSON_strdup(string);
}
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = cJSON_Array;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = cJSON_Object;
return item;
}创建完一个根结点结构体后,接下来就是向根结点中加入元素。
从头文件我们发现,cJSON_AddStringToObject()等其实是宏定义,本质上调用的都是cJSON_AddItemToObject()函数,在cJSON.h文件中可以看到如下定义:
// 利用宏函数来快速增加cJSON相关节点信息
// 创建一个string值为name的cJSON_Null节点,并添加到object
#define cJSON_AddNullToObject(object,name) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateNull())
// 创建一个string值为name的cJSON_True节点,并添加到object
#define cJSON_AddTrueToObject(object,name) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateTrue())
// 创建一个string值为name的cJSON_False节点,并添加到object
#define cJSON_AddFalseToObject(object,name) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateFalse())
// 创建一个string值为name的cJSON_CreateBool节点,并添加到object。b非0为cJSON_True,0为cJSON_False。
#define cJSON_AddBoolToObject(object,name,b) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateBool(b))
// 创建一个string值为name,valuedouble为n,valueint为(int)n的cJSON_Number节点,并添加到object。
#define cJSON_AddNumberToObject(object,name,n) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateNumber(n))
// 创建一个string值为name,valuestring为s的cJSON_String节点,并添加到object。
#define cJSON_AddStringToObject(object,name,s) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateString(s))过程是调用cJSON_AddItemToObject()并结合不同的对象类型增加节点名称和子节点。然后在其中调用cJSON_AddItemToArray()函数来添加信息,此函数中判断对象孩子结点是否为NULL,如果是NULL,则直接插入,否则找到最后一个孩子,调用suffix_object()函数添加到双向链表的尾部。
示例图如下:
相关代码如下:
// 将字符串添加进对象
void cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item)
{
if (!item)
return;
if (item->string)
cJSON_free(item->string); // 这个儿子之前有key,先清理
item->string=cJSON_strdup(string); // 设置key值
cJSON_AddItemToArray(object,item); // 添加儿子
}
// 将传入的字符串复制一副本并返回新的字符串指针
static char* cJSON_strdup(const char* str)
{
size_t len;
char* copy;
len = strlen(str) + 1;
// 分配空间
if (!(copy = (char*)cJSON_malloc(len)))
return 0;
// 执行复制操作
memcpy(copy,str,len);
// 返回复制的副本
return copy;
}
// 添加节点到object或array中
void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item)
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
if (!item)
return;
if (!c)
{
array->child=item; // 之前不存在儿子节点,直接添加
}
else
{
while (c && c->next) // 先找到最后一个儿子
c=c->next;
suffix_object(c,item); // 添加儿子,c是item的兄弟节点
}
}
// array的处理
static void suffix_object(cJSON *prev,cJSON *item)
{
// 两个兄弟的指针互相指向对方
prev->next=item;
item->prev=prev;
}cjson打印:
cjson打印就是从根对象的结构体开始遍历,得到每个item结点的名称和数据,并经过处理成特定的cjson字符串的输出形式。
cJSON_Print(root)和cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root) 函数都是打印成json字符串的函数,两者的区别就是
cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root) 处理成的字符串里没有\t\n这类的格式,我们在这里以分析cJSON_Print(root)函数
为例,进行分析。
相关函数结构图如下:
相关函数如下:
typedef struct {
char *buffer;
int length;
int offset;
} printbuffer;
static int pow2gt(int x) /*返回 一个比x的n(其中n是2的幂),并且是最小的幂,说白了就是将一个数后边所有的位都置1然后再+1*/
{
--x;
x |= x >> 1;
x |= x >> 2;
x |= x >> 4;
x |= x >> 8;
x |= x >> 16;
return x + 1;
}
/* ensure 函数 是一个 协助 printbuffer 分配内存的一个函数
* len 表示当前字符串的字符串起始偏移量 即 newbuffer+p->offset 起始的
*/
static char* ensure(printbuffer *p,int needed)
{
char *newbuffer;int newsize;
if (!p || !p->buffer) return 0;//传入参数合法性检测
needed+=p->offset;//需要额外分配的内存 也就是偏移量
if (needed<=p->length) return p->buffer+p->offset;//内存够用直接返回
newsize=pow2gt(needed);
newbuffer=(char*)cJSON_malloc(newsize);//malloc出新内存 放buffer里面的内容
if (!newbuffer) {cJSON_free(p->buffer);p->length=0,p->buffer=0;return 0;}
if (newbuffer) memcpy(newbuffer,p->buffer,p->length);//
cJSON_free(p->buffer);//
p->length=newsize;
p->buffer=newbuffer;
return newbuffer+p->offset;//
}
char *cJSON_Print(cJSON * item)
{
return print_value(item, 0, 1, 0);
}
static char *print_value(cJSON * item, int depth, int fmt, printbuffer * p)
{
char *out = 0;
if (!item)
return 0;
if (p) {
switch ((item->type) & 255) {
case cJSON_NULL:{
out = ensure(p, 5);
if (out)
strcpy(out, "null");
break;
}
case cJSON_False:{
out = ensure(p, 6);
if (out)
strcpy(out, "false");
break;
}
case cJSON_True:{
out = ensure(p, 5);
if (out)
strcpy(out, "true");
break;
}
case cJSON_Number:
out = print_number(item, p); //打印数字函数
break;
case cJSON_String:
out = print_string(item, p); //打印字符串函数
break;
case cJSON_Array:
out = print_array(item, depth, fmt, p); //打印数组函数
break;
case cJSON_Object:
out = print_object(item, depth, fmt, p); //打印object对象类型的函数
break;
}
} else {
switch ((item->type) & 255) {
case cJSON_NULL:
out = cJSON_strdup("null");
break;
case cJSON_False:
out = cJSON_strdup("false");
break;
case cJSON_True:
out = cJSON_strdup("true");
break;
case cJSON_Number:
out = print_number(item, 0);
break;
case cJSON_String:
out = print_string(item, 0);
break;
case cJSON_Array:
out = print_array(item, depth, fmt, 0);
break;
case cJSON_Object:
out = print_object(item, depth, fmt, 0);
break;
}
}
return out;
}
static char *print_number(cJSON * item, printbuffer * p) //打印数字函数
{
char *str = 0;
double d = item->valuedouble;
if (d == 0) {
if (p)
str = ensure(p, 2);
else
str = (char *) cJSON_malloc(2); /* special case for 0. */
if (str)
strcpy(str, "0");
} else if (fabs(((double) item->valueint) - d) <= DBL_EPSILON
&& d <= INT_MAX && d >= INT_MIN) {
if (p)
str = ensure(p, 21);
else
str = (char *) cJSON_malloc(21); /* 2 ^ 64 + 1可以用21个字符表示 */
if (str)
sprintf(str, "%d", item->valueint);
} else {
if (p)
str = ensure(p, 64);
else
str = (char *) cJSON_malloc(64); /* This is a nice tradeoff. */
if (str) {
if (fpclassify(d) != FP_ZERO && !isnormal(d)) //非正常浮点数
sprintf(str, "null");
else if (fabs(floor(d) - d) <= DBL_EPSILON
&& fabs(d) < 1.0e60)
sprintf(str, "%.0f", d);
else if (fabs(d) < 1.0e-6 || fabs(d) > 1.0e9)
sprintf(str, "%e", d);
else
sprintf(str, "%f", d);
}
}
return str;
}
static char *print_string(cJSON * item, printbuffer * p) //打印字符串类型的结点
{
return print_string_ptr(item->valuestring, p);
}
static char *print_string_ptr(const char *str, printbuffer * p) //打印字符串类型的结点
{
const char *ptr;
char *ptr2, *out;
int len = 0, flag = 0;
unsigned char token;
if (!str) {
if (p)
out = ensure(p, 3);
else
out = (char *) cJSON_malloc(3);
if (!out)
return 0;
strcpy(out, "\"\""); //字符串为空
return out;
}
for (ptr = str; *ptr; ptr++)
flag |= ((*ptr > 0 && *ptr < 32) || (*ptr == '\"')
|| (*ptr == '\\')) ? 1 : 0;
if (!flag) { //对字符串中不含'\','/',空格等字符的字符处理
len = ptr - str;
if (p)
out = ensure(p, len + 3);
else
out = (char *) cJSON_malloc(len + 3);
if (!out)
return 0;
ptr2 = out;
*ptr2++ = '\"';
strcpy(ptr2, str);
ptr2[len] = '\"';
ptr2[len + 1] = 0;
return out;
}
ptr = str;
while ((token = *ptr) && ++len) {
if (strchr("\"\\\b\f\n\r\t", token))
len++;
else if (token < 32)
len += 5;
ptr++;
}
if (p)
out = ensure(p, len + 3);
else
out = (char *) cJSON_malloc(len + 3);
if (!out)
return 0;
ptr2 = out;
ptr = str;
*ptr2++ = '\"';
while (*ptr) {
if ((unsigned char) *ptr > 31 && *ptr != '\"'
&& *ptr != '\\')
*ptr2++ = *ptr++;
else {
*ptr2++ = '\\';
switch (token = *ptr++) {
case '\\':
*ptr2++ = '\\';
break;
case '\"':
*ptr2++ = '\"';
break;
case '\b':
*ptr2++ = 'b';
break;
case '\f':
*ptr2++ = 'f';
break;
case '\n':
*ptr2++ = 'n';
break;
case '\r':
*ptr2++ = 'r';
break;
case '\t':
*ptr2++ = 't';
break;
default:
sprintf(ptr2, "u%04x", token);
ptr2 += 5;
break; /* escape and print */
}
}
}
*ptr2++ = '\"';
*ptr2++ = 0;
return out;
}
static char *print_array(cJSON * item, int depth, int fmt, printbuffer * p) //打印数组类型结点函数
{
char **entries;
char *out = 0, *ptr, *ret;
int len = 5;
cJSON *child = item->child;
int numentries = 0, i = 0, fail = 0;
size_t tmplen = 0;
/* 数组里有多少个元素 */
while (child)
numentries++, child = child->next;
/* 明确处理numentries = = 0 */ //处理空数组
if (!numentries) {
if (p)
out = ensure(p, 3);
else
out = (char *) cJSON_malloc(3);
if (out)
strcpy(out, "[]");
return out;
}
if (p) {
/* 组成数组的输出形式 */
i = p->offset;
ptr = ensure(p, 1);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
*ptr = '[';
p->offset++;
child = item->child;
while (child && !fail) {
print_value(child, depth + 1, fmt, p);
p->offset = update(p);
if (child->next) {
len = fmt ? 2 : 1;
ptr = ensure(p, len + 1);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
*ptr++ = ',';
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = ' ';
*ptr = 0;
p->offset += len;
}
child = child->next;
}
ptr = ensure(p, 2);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
*ptr++ = ']';
*ptr = 0;
out = (p->buffer) + i;
} else {
/* 分配一个指针数组存储数组里的每一个元素的打印结果 */
entries =
(char **) cJSON_malloc(numentries * sizeof(char *));
if (!entries)
return 0;
memset(entries, 0, numentries * sizeof(char *));
/* 检索所有结果: */
child = item->child;
while (child && !fail) {
ret = print_value(child, depth + 1, fmt, 0);
entries[i++] = ret;
if (ret)
len += strlen(ret) + 2 + (fmt ? 1 : 0);
else
fail = 1;
child = child->next;
}
if (!fail)
out = (char *) cJSON_malloc(len);
if (!out)
fail = 1;
if (fail) {
for (i = 0; i < numentries; i++)
if (entries[i])
cJSON_free(entries[i]);
cJSON_free(entries);
return 0;
}
/* 组成数组的输出形式. */
*out = '[';
ptr = out + 1;
*ptr = 0;
for (i = 0; i < numentries; i++) {
tmplen = strlen(entries[i]);
memcpy(ptr, entries[i], tmplen);
ptr += tmplen;
if (i != numentries - 1) {
*ptr++ = ',';
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = ' ';
*ptr = 0;
}
cJSON_free(entries[i]);
}
cJSON_free(entries);
*ptr++ = ']';
*ptr++ = 0;
}
return out;
}
/* 打印object类型结点. */
static char *print_object(cJSON * item, int depth, int fmt, printbuffer * p)
{
char **entries = 0, **names = 0;
char *out = 0, *ptr, *ret, *str;
int len = 7, i = 0, j;
cJSON *child = item->child;
int numentries = 0, fail = 0;
size_t tmplen = 0;
/* 统计有多少个子结点. */
while (child)
numentries++, child = child->next;
/* 明确处理空对象的情况*/
if (!numentries) {
if (p)
out = ensure(p, fmt ? depth + 4 : 3);
else
out = (char *) cJSON_malloc(fmt ? depth + 4 : 3);
if (!out)
return 0;
ptr = out;
*ptr++ = '{';
if (fmt) {
*ptr++ = '\n';
for (i = 0; i < depth; i++)
*ptr++ = '\t';
}
*ptr++ = '}';
*ptr++ = 0;
return out;
}
if (p) {
/* 组成输出形式: */
i = p->offset;
len = fmt ? 2 : 1;
ptr = ensure(p, len + 1);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
*ptr++ = '{';
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = '\n';
*ptr = 0;
p->offset += len;
child = item->child;
depth++;
while (child) {
if (fmt) {
ptr = ensure(p, depth);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
for (j = 0; j < depth; j++)
*ptr++ = '\t';
p->offset += depth;
}
print_string_ptr(child->string, p);
p->offset = update(p);
len = fmt ? 2 : 1;
ptr = ensure(p, len);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
*ptr++ = ':';
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = '\t';
p->offset += len;
print_value(child, depth, fmt, p);
p->offset = update(p);
len = (fmt ? 1 : 0) + (child->next ? 1 : 0);
ptr = ensure(p, len + 1);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
if (child->next)
*ptr++ = ',';
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = '\n';
*ptr = 0;
p->offset += len;
child = child->next;
}
ptr = ensure(p, fmt ? (depth + 1) : 2);
if (!ptr)
return 0;
if (fmt)
for (i = 0; i < depth - 1; i++)
*ptr++ = '\t';
*ptr++ = '}';
*ptr = 0;
out = (p->buffer) + i;
} else {
/*为对象和名称分配空间 */
entries =
(char **) cJSON_malloc(numentries * sizeof(char *));
if (!entries)
return 0;
names =
(char **) cJSON_malloc(numentries * sizeof(char *));
if (!names) {
cJSON_free(entries);
return 0;
}
memset(entries, 0, sizeof(char *) * numentries);
memset(names, 0, sizeof(char *) * numentries);
/* 将所有结果收集到数组: */
child = item->child;
depth++;
if (fmt)
len += depth;
while (child && !fail) {
names[i] = str =
print_string_ptr(child->string, 0);
entries[i++] = ret =
print_value(child, depth, fmt, 0);
if (str && ret)
len +=
strlen(ret) + strlen(str) + 2 +
(fmt ? 2 + depth : 0);
else
fail = 1;
child = child->next;
}
if (!fail)
out = (char *) cJSON_malloc(len);
if (!out)
fail = 1;
if (fail) {
for (i = 0; i < numentries; i++) {
if (names[i])
cJSON_free(names[i]);
if (entries[i])
cJSON_free(entries[i]);
}
cJSON_free(names);
cJSON_free(entries);
return 0;
}
/* 组成输出形式: */
*out = '{';
ptr = out + 1;
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = '\n';
*ptr = 0;
for (i = 0; i < numentries; i++) {
if (fmt)
for (j = 0; j < depth; j++)
*ptr++ = '\t';
tmplen = strlen(names[i]);
memcpy(ptr, names[i], tmplen);
ptr += tmplen;
*ptr++ = ':';
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = '\t';
strcpy(ptr, entries[i]);
ptr += strlen(entries[i]);
if (i != numentries - 1)
*ptr++ = ',';
if (fmt)
*ptr++ = '\n';
*ptr = 0;
cJSON_free(names[i]);
cJSON_free(entries[i]);
}
cJSON_free(names);
cJSON_free(entries);
if (fmt)
for (i = 0; i < depth - 1; i++)
*ptr++ = '\t';
*ptr++ = '}';
*ptr++ = 0;
}
return out;
}cJSON解析:
首先,调用cJSON_Parse()函数,此函数是一个二次封装函数,其内部为cJSON_ParseWithOpts()函数,该函数用于提取更多的解析选项,如果需要,最后返回解析结束的位置。而在上面的函数中,调用parse_value()函数进行解析,而该函数首先创建cJSON_NewItem()创建节点,用于存放解析的JSON结构数据,然后根据不同的选项,调用解析函数,其为parse_string(),parse_number(),parse_array(),parse_objec()等。
结构图如下:
相关函数如下:
// cJSON解析的二次封装函数
cJSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value)
{
return cJSON_ParseWithOpts(value,0,0);
}
// 解析对象,创建一个新的根并初始化,返回一个cJSON类型
cJSON *cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value,const char **return_parse_end,int require_null_terminated)
{
const char *end=0;
cJSON *c=cJSON_New_Item(); //创建一个新结点
ep=0; //ep为全局变量,错误信息就保存在全局字符串指针ep里,调用cJSON_GetErrorPtr()可以得要错误原因的描述字符串
if (!c)
return 0;
end=parse_value(c,skip(value));
if (!end)
{
cJSON_Delete(c);
return 0;
} /* parse failure. ep is set. */
/* if we require null-terminated JSON without appended garbage, skip and then check for a null terminator */
if (require_null_terminated)
{
end=skip(end);
if (*end)
{
cJSON_Delete(c);
ep=end;
return 0;
}
}
if (return_parse_end)
*return_parse_end=end;
return c;
}
// 解析器核心函数
static const char *parse_value(cJSON *item,const char *value)
{
if (!value)
return 0; /* Fail on null. */
if (!strncmp(value,"null",4))
{
item->type=cJSON_NULL;
return value+4;
}
if (!strncmp(value,"false",5))
{
item->type=cJSON_False;
return value+5;
}
if (!strncmp(value,"true",4))
{
item->type=cJSON_True;
item->valueint=1;
return value+4;
}
if (*value=='\"')
{
return parse_string(item,value);
}
if (*value=='-' || (*value>='0' && *value<='9'))
{
return parse_number(item,value);
}
if (*value=='[')
{
return parse_array(item,value);
}
if (*value=='{')
{
return parse_object(item,value);
}
ep=value;
return 0; /* failure. */
}
static const char *parse_string(cJSON *item,const char *str) //解析字符串函数
{
const char *ptr=str+1;
char *ptr2;
char *out;
int len=0;
unsigned uc,uc2;
if (*str!='\"') // 不是字符串情况
{
ep=str;
return 0;
} /* not a string! */
while (*ptr!='\"' && *ptr && ++len)
if (*ptr++ == '\\')
ptr++; // 跳出前面的引用
out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+1); /* This is how long we need for the string, roughly. */
if (!out)
return 0;
ptr=str+1;
ptr2=out;
while (*ptr!='\"' && *ptr)
{
if (*ptr!='\\')
*ptr2++=*ptr++;
else
{
ptr++;
switch (*ptr)
{
case 'b': *ptr2++='\b'; break;
case 'f': *ptr2++='\f'; break;
case 'n': *ptr2++='\n'; break;
case 'r': *ptr2++='\r'; break;
case 't': *ptr2++='\t'; break;
case 'u': /* transcode utf16 to utf8. */
uc=parse_hex4(ptr+1);
ptr+=4; /* get the unicode char. */
if ((uc>=0xDC00 && uc<=0xDFFF) || uc==0)
break; /* check for invalid. */
if (uc>=0xD800 && uc<=0xDBFF) /* UTF16 surrogate pairs. */
{
if (ptr[1]!='\\' || ptr[2]!='u')
break; /* missing second-half of surrogate. */
uc2=parse_hex4(ptr+3);ptr+=6;
if (uc2<0xDC00 || uc2>0xDFFF)
break; /* invalid second-half of surrogate. */
uc=0x10000 + (((uc&0x3FF)<<10) | (uc2&0x3FF));
}
len=4;
if (uc<0x80)
len=1;
else if (uc<0x800)
len=2;
else if (uc<0x10000)
len=3;
ptr2+=len;
switch (len)
{
case 4: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;
case 3: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;
case 2: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;
case 1: *--ptr2 =(uc | firstByteMark[len]);
}
ptr2+=len;
break;
default: *ptr2++=*ptr; break;
}
ptr++;
}
}
*ptr2=0;
if (*ptr=='\"') ptr++;
item->valuestring=out;
item->type=cJSON_String;
return ptr;
}
// 跳过这些空格,这里跳过了ascii值小于32的。
static const char *skip(const char *in)
{
while (in && *in && (unsigned char)*in<=32)
in++;
return in;
}
// parse_number函数功能:解析数字,对输入的文本生成一个数字,并填充结果项,传入参数有两
// 个,这里先只关注num,返回值是一个字符串
static const char *parse_number(cJSON *item,const char *num)
{
double n=0,sign=1,scale=0;
int subscale=0,signsubscale=1;
if (*num=='-') sign=-1,num++; // 判断数字是否是有符号数字
if (*num=='0') num++; // 判断数字是否为0
if (*num>='1' && *num<='9')
do // 转换数字
n=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0');
while (*num>='0' && *num<='9');
if (*num=='.' && num[1]>='0' && num[1]<='9') // 对小数点后边的部分进行处理,scale记录小数点后边的位数
{
num++;
do
n=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0'),scale--; // scale为小数点后的位数
while (*num>='0' && *num<='9');
}
if (*num=='e' || *num=='E') // 是否为指数,科学计数法
{
num++;
if (*num=='+') // 判断指数后边幂的正负号
num++;
else if (*num=='-')
signsubscale=-1,num++;
while (*num>='0' && *num<='9') // 处理指数后边10的幂
subscale=(subscale*10)+(*num++ - '0');
}
// 将字符串转换为相应的数值
n=sign*n*pow(10.0,(scale+subscale*signsubscale)); /* number = +/- number.fraction * 10^+/- exponent */
item->valuedouble=n; // 将算出来的值存入缓存
item->valueint=(int)n; // 将算出来的值存入缓存
item->type=cJSON_Number; // 目标类型为数字
return num;
}
// 从输入文本中构建array
static const char *parse_array(cJSON *item,const char *value)
{
cJSON *child;
if (*value!='[') {ep=value;return 0;} /* not an array! */
item->type=cJSON_Array;
value=skip(value+1);
if (*value==']') return value+1; /* empty array. */
item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item();
if (!item->child) return 0; /* memory fail */
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */
if (!value) return 0;
while (*value==',')
{
cJSON *new_item;
if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */
child->next=new_item;new_item->prev=child;child=new_item;
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1)));
if (!value) return 0; /* memory fail */
}
if (*value==']') return value+1; /* end of array */
ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */
}
// 从输入文本中构建object
static const char *parse_object(cJSON *item,const char *value)
{
cJSON *child;
if (*value!='{') {ep=value;return 0;} /* not an object! */
item->type=cJSON_Object;
value=skip(value+1);
if (*value=='}') return value+1; /* empty array. */
item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item();
if (!item->child) return 0;
value=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value)));
if (!value) return 0;
child->string=child->valuestring;child->valuestring=0;
if (*value!=':') {ep=value;return 0;} /* fail! */
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */
if (!value) return 0;
while (*value==',')
{
cJSON *new_item;
if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */
child->next=new_item;new_item->prev=child;child=new_item;
value=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value+1)));
if (!value) return 0;
child->string=child->valuestring;child->valuestring=0;
if (*value!=':') {ep=value;return 0;} /* fail! */
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */
if (!value) return 0;
}
if (*value=='}') return value+1; /* end of array */
ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */
}
// 将十六进制的字符串转换为数字表示!
static unsigned parse_hex4(const char *str)
{
unsigned h=0;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9')
h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F')
h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f')
h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else
return 0;
h=h<<4;str++;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9')
h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F')
h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f')
h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else
return 0;
h=h<<4;str++;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9')
h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F')
h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f')
h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else
return 0;
h=h<<4;str++;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9')
h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F')
h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f')
h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else
return 0;
return h;
}cJSON内存管理:
hook管理函数:
在 c 语言中内存一般是 malloc 和 free 的。
为了方便用户自由的管理内存, cjson 使用 Hook 技术来让使用者可以自定义内存管理函数。
即用户自定义 malloc 和 free.
具体实现方式可以参考下面的代码, 默认使用系统的 malloc 和 free 函数, 用过 cJSON_InitHooks 函数可以替换成用户自定义的 malloc 和 free 函数。
typedef struct cJSON_Hooks
{
void *(*malloc_fn)(size_t sz);
void (*free_fn)(void *ptr);
} cJSON_Hooks;
// 对cJSON提供的分配,再分配,释放内存初始化函数
extern void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks);
// 默认将分配和释放空间函数指针指向malloc和free
static void *(*cJSON_malloc)(size_t sz) = malloc;
static void (*cJSON_free)(void *ptr) = free;
// 其使用Hook技术来让使用者可以自定义内存管理函数。其中默认系统使用的内存分配和释放函数是malloc
// 和free函数,利用cJSON_InitHooks函数可以替换成用户自定义的malloc和free函数。
void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks)
{
// 如果未定义,则使用默认的malloc和free函数
if (!hooks) { /* Reset hooks */
cJSON_malloc = malloc;
cJSON_free = free;
return;
}
// 定义了,则使用用户自定义的malloc和free函数
cJSON_malloc = (hooks->malloc_fn)?hooks->malloc_fn:malloc;
cJSON_free = (hooks->free_fn)?hooks->free_fn:free;
}
cJSON的删除:
删除节点很简单, 先删除儿子,然后清理内存即可。
总结一下就是对于 object 和 array 需要先删除儿子,然后删除自己。
对于 字符串, 需要先释放字符串的内存, 再释放自己这块内存。
对于其他节点,直接释放自己这块内存。
/*删除结点函数*/
void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c) {
cJSON *next;
while (c) {
next=c->next;
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->child) cJSON_Delete(c->child);
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->valuestring) cJSON_free(c->valuestring);
if (c->string) cJSON_free(c->string);
cJSON_free(c);
c=next;
}
}
/*删除儿子结点函数*/
删除也是从 array 和 object 中删除,实现就比较简洁了。
void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which) {
cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(array,which));
}
void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string) {
cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(object,string));
}我们把一个节点从 json 树中删除, 但是不释放内存,而是先保留这个节点的指针, 这样储存在这个节点的信息都保留了下来。
接下来我们就可以做很多事了, 合适的时候添加到其他对象中, 合适的时候释放内存。
比如上面的 delete 函数, 就需要真实的删除了, 这个时候我们删除即可。
而 detach 实现也比较简单, 只是少了一步删除操作。
// 节点从双向链表中删除即可
cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which) {
cJSON *c=array->child;
while (c && which>0) c=c->next,which--;
if (!c) return 0;
if (c->prev) c->prev->next=c->next;
if (c->next) c->next->prev=c->prev;
if (c==array->child) array->child=c->next;
c->prev=c->next=0;
return c;
}
cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string) {
int i=0;
cJSON *c=object->child;
while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string)) i++,c=c->next;
if (c) return cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(object,i);
return 0;
}
其他函数:
前面我们已经将json功能分为三大块进行了解析,现在把剩余的一些函数贴上,这些函数单独分析即可。
// 返回节点的个数
int cJSON_GetArraySize(cJSON *array)
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
int i=0;
while(c)
i++,c=c->next;
return i;
}
// 返回array中第item个节点的地址
cJSON *cJSON_GetArrayItem(cJSON *array,int item)
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
while (c && item>0)
item--,c=c->next;
return c;
}
// 返回Object中第item个节点的地址
cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string)
{
cJSON *c=object->child;
while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string))
c=c->next;
return c;
}
//在链表中插入一个新结点
void cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem)
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
// 找到which位置
while (c && which>0)
c=c->next,which--;
// 添加新的节点到array中
if (!c)
{
cJSON_AddItemToArray(array,newitem);
return;
}
// 将链表节点进行挂接
newitem->next=c;
newitem->prev=c->prev;
c->prev=newitem;
// 处理arrya的孩子节点
if (c==array->child)
array->child=newitem;
else
newitem->prev->next=newitem;
}
// 替换节点操作,用新的节点替换原有的某一个节点
void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem)
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
// 找到which位置
while (c && which>0)
c=c->next,which--;
if (!c)
return;
// 进行挂接
newitem->next=c->next;
newitem->prev=c->prev;
// 处理NULL情况
if (newitem->next)
newitem->next->prev=newitem;
// 处理孩子节点
if (c==array->child)
array->child=newitem;
else
newitem->prev->next=newitem;
c->next=c->prev=0;
// 删除替换的节点
cJSON_Delete(c);
}
// 替换节点操作
// 用原有节点替换现有节点
void cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem)
{
int i=0;
cJSON *c=object->child;
while(c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string))
i++,c=c->next;
if(c)
{
newitem->string=cJSON_strdup(string);
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(object,i,newitem);
}
}
// 拷贝副本操作
cJSON *cJSON_Duplicate(cJSON *item,int recurse)
{
cJSON *newitem,*cptr,*nptr=0,*newchild;
/* Bail on bad ptr */
if (!item)
return 0;
/* Create new item */
newitem=cJSON_New_Item();
if (!newitem)
return 0;
/* Copy over all vars */
newitem->type=item->type&(~cJSON_IsReference),newitem->valueint=item->valueint,newitem->valuedouble=item->valuedouble;
if (item->valuestring)
{
newitem->valuestring=cJSON_strdup(item->valuestring);
if (!newitem->valuestring)
{
cJSON_Delete(newitem);
return 0;
}
}
if (item->string)
{
newitem->string=cJSON_strdup(item->string);
if (!newitem->string)
{
cJSON_Delete(newitem);
return 0;
}
}
/* If non-recursive, then we're done! */
if (!recurse)
return newitem;
/* Walk the ->next chain for the child. */
cptr=item->child;
while (cptr)
{
newchild=cJSON_Duplicate(cptr,1); /* Duplicate (with recurse) each item in the ->next chain */
if (!newchild)
{
cJSON_Delete(newitem);
return 0;
}
if (nptr)
{
nptr->next=newchild,newchild->prev=nptr;
nptr=newchild;
} /* If newitem->child already set, then crosswire ->prev and ->next and move on */
else
{
newitem->child=newchild;
nptr=newchild;
} /* Set newitem->child and move to it */
cptr=cptr->next;
}
return newitem;
}