Polar bears Menshykov and Uslada from the zoo of St. Petersburg and elephant Horace from the zoo of Kiev decided to build a house of cards. For that they've already found a hefty deck of n playing cards. Let's describe the house they want to make:
- The house consists of some non-zero number of floors.
- Each floor consists of a non-zero number of rooms and the ceiling. A room is two cards that are leaned towards each other. The rooms are made in a row, each two adjoining rooms share a ceiling made by another card.
- Each floor besides for the lowest one should contain less rooms than the floor below.
Please note that the house may end by the floor with more than one room, and in this case they also must be covered by the ceiling. Also, the number of rooms on the adjoining floors doesn't have to differ by one, the difference may be more.
While bears are practicing to put cards, Horace tries to figure out how many floors their house should consist of. The height of the house is the number of floors in it. It is possible that you can make a lot of different houses of different heights out of n cards. It seems that the elephant cannot solve this problem and he asks you to count the number of the distinct heights of the houses that they can make using exactly n cards.
The single line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1012) — the number of cards.
Print the number of distinct heights that the houses made of exactly n cards can have.
13
1
6
0
In the first sample you can build only these two houses (remember, you must use all the cards):
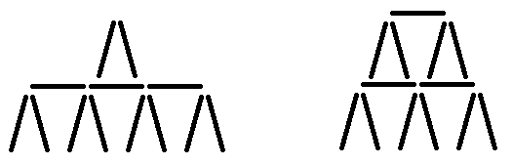
Thus, 13 cards are enough only for two floor houses, so the answer is 1.
The six cards in the second sample are not enough to build any house.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define rep(i,m,n) for(int i=m;i<=n;i++)
#define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
const int inf_int = 2e9;
const long long inf_ll = 2e18;
#define inf_add 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define Lson L, mid, rt<<1
#define Rson mid+1, R, rt<<1|1
const int maxn=5e2+10;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline int read(){int ra,fh;char rx;rx=getchar(),ra=0,fh=1;
while((rx<'0'||rx>'9')&&rx!='-')rx=getchar();if(rx=='-')
fh=-1,rx=getchar();while(rx>='0'&&rx<='9')ra*=10,ra+=rx-48,
rx=getchar();return ra*fh;}
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;}
typedef vector<int> vi;
int dir[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
const int N = 1e7+5;
ll n;
ll ct=0;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;;i++)
{
ll t = (ll)i*(ll)(i-1)/(ll)2*(ll)3+(ll)2*i;
if(t<=n)
{
if((n-t)%3==0)
ct++;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
cout << ct<<endl;
return 0;
}