高性能定时器(一)
先来三句口号
我们通常所说的定时器是定时器容器,是容器类数据结构。
定时器是容器内容纳的一个对象,是对定时器的封装。
我们通常所说的定时器是定时器容器,是容器类数据结构。
定时器是容器内容纳的一个对象,是对定时器的封装。
我们通常所说的定时器是定时器容器,是容器类数据结构。
定时器是容器内容纳的一个对象,是对定时器的封装。
前几日学习了一下定时器
首先吐槽一下,最近学的东西感觉都听上去很高大上,但是自己一接触发现也就那么回事,像是一位长发飘飘的白衣女子,可是又何必回身过来乱了芳华。
哈哈哈,废话就不多说了。
开篇题为高性能定时器,这次呢我们根据定时器的种类大致上分为三个模块,基于链表的定时器,还有两个比较常用的高性能定时器,时间轮和时间堆
不过在具体地讨论如何组织定时器之前,我们先要介绍一下定时的方法。定时是指在一段时间后触发某段代码的机制。换言之,定时器机制是定时器得以被处理的原动力。linux 提供三种方法,如下所示:
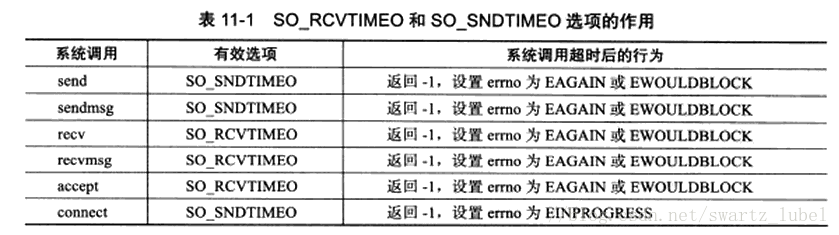
- socket选项SO_RCVTIMEO 和 SO_SNDTIMEO
- SIGALRM 信号
- I/O 复用系统调用的超时参数
socket选项SO_RCVTIMEO 和 SO_SNDTIMEO
setsockopt( SOCKET s, int level, int optname, const char FAR* optval, int option);
第三个参数optname可用来指定超时接受(SO_RCVTIMEO)或者超时发送(SO_SNDTIMEO),与其关联的第四个参数此时为timeout类型,指定具体的超时时间。然后用connect()函数去连接客户端,超时对应的errno是EINPROGRESS。检测到此errno则关闭连接。此处根据系统调用的返回值来判断超时时间是否已到,据此处理定时任务即关闭连接。这两个选项分别用来设置socket接收数据和发送数据的超时时间,因此仅对于数据接收和发送相关的socket专用系统调用有效,这些系统调用包括 send,sendmsg,recv,recvmsg ,accept 和connect.
话不多说,都在代码里了
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int timeout_connect( const char* ip, int port, int time )
{
int ret = 0;
struct sockaddr_in address;
bzero( &address, sizeof( address ) );
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton( AF_INET, ip, &address.sin_addr );
address.sin_port = htons( port );
int sockfd = socket( PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 );
assert( sockfd >= 0 );
struct timeval timeout;
timeout.tv_sec = time;
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
socklen_t len = sizeof( timeout );
ret = setsockopt( sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDTIMEO, &timeout, len );
assert( ret != -1 );
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
~~/* 如何触发这个条件
* 我突然想到的办法是让服务器在accept之前阻塞一会儿
* 有没有服务器命令可以帮我完成这个事情
*
* 原来是可以的啊
*/~~
**2018.1.18 这个想法是完全错误的!!!**
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
ret = connect( sockfd, ( struct sockaddr* )&address, sizeof( address ) );
if ( ret == -1 )
{
if( errno == EINPROGRESS )
{
printf( "connecting timeout\n" );
return -1;
}
printf( "error occur when connecting to server\n" );
return -1;
}
return sockfd;
}
int main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{
if( argc <= 2 )
{
printf( "usage: %s ip_address port_number\n", basename( argv[0] ) );
return 1;
}
const char* ip = argv[1];
int port = atoi( argv[2] );
int sockfd = timeout_connect( ip, port, 10 );
if ( sockfd < 0 )
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
./a.out localhost 8888 执行
然后就成功啦
进行修正
2018.1.18
连接一个不可达的服务器就可以触发此条件
如 ./a.out 127.24.234.234 8989
地址和端口随便填一个就可以了 千万不能是已经打开的服务器程序就好!!!
关于具体原因 我会在随后更新的博文会提及到
2018.1.19
触发connect超时事件
关于SIGALRM
除了通过系统调用来处理,更多的是使用信号。SIGALRM是在定时器终止时发送给进程的信号。由alarm()和setitimer()函数设置的实时闹钟一旦超时,将触发此信号,然后在其处理函数中处理到期的任务。
这一部分我问通过如下的这个实例来说明—处理非活动连接,来介绍如何使用SIGALRM,
基于链表的定时器
首先我们要使用 SIGALRM, 我们在此引入了一种简单定时器—基于生序链表实现的定时器,这里的双向链表没有使用容器 list , 这个大家可以自己去实现一下, 类代码如下所示:
#ifndef LST_TIMER
#define LST_TIMER
#include <time.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 64
class util_timer;
struct client_data
{
sockaddr_in address;
int sockfd;
char buf[ BUFFER_SIZE ];
util_timer* timer;
};
class util_timer
{
public:
util_timer() : prev( NULL ), next( NULL ){}
public:
time_t expire;
void (*cb_func)( client_data* );
client_data* user_data;
util_timer* prev;
util_timer* next;
};
class sort_timer_lst
{
public:
sort_timer_lst() : head( NULL ), tail( NULL ) {}
~sort_timer_lst()
{
util_timer* tmp = head;
while( tmp )
{
head = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
tmp = head;
}
}
void add_timer( util_timer* timer )
{
if( !timer )
{
return;
}
if( !head )
{
head = tail = timer;
return;
}
if( timer->expire < head->expire )
{
timer->next = head;
head->prev = timer;
head = timer;
return;
}
add_timer( timer, head );
}
void adjust_timer( util_timer* timer )
{
if( !timer )
{
return;
}
util_timer* tmp = timer->next;
if( !tmp || ( timer->expire < tmp->expire ) )
{
return;
}
if( timer == head )
{
head = head->next;
head->prev = NULL;
timer->next = NULL;
add_timer( timer, head );
}
else
{
timer->prev->next = timer->next;
timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
add_timer( timer, timer->next );
}
}
void del_timer( util_timer* timer )
{
if( !timer )
{
return;
}
if( ( timer == head ) && ( timer == tail ) )
{
delete timer;
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
return;
}
if( timer == head )
{
head = head->next;
head->prev = NULL;
delete timer;
return;
}
if( timer == tail )
{
tail = tail->prev;
tail->next = NULL;
delete timer;
return;
}
timer->prev->next = timer->next;
timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
delete timer;
}
void tick()
{
if( !head )
{
return;
}
printf( "timer tick\n" );
time_t cur = time( NULL );
util_timer* tmp = head;
while( tmp )
{
if( cur < tmp->expire )
{
break;
}
tmp->cb_func( tmp->user_data );
head = tmp->next;
if( head )
{
head->prev = NULL;
}
delete tmp;
tmp = head;
}
}
private:
void add_timer( util_timer* timer, util_timer* lst_head )
{
util_timer* prev = lst_head;
util_timer* tmp = prev->next;
while( tmp )
{
if( timer->expire < tmp->expire )
{
prev->next = timer;
timer->next = tmp;
tmp->prev = timer;
timer->prev = prev;
break;
}
prev = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if( !tmp )
{
prev->next = timer;
timer->prev = prev;
timer->next = NULL;
tail = timer;
}
}
private:
util_timer* head;
util_timer* tail;
};
#endif
现在我们来考虑实际应用,服务器一般在内核可以通过设置socket选项KEEPALIVE 来激活客户端,但这样会使对连接的管理变得复杂,因此我们在应用层来实现类似机制,以管理处于非活动客户端。如下使用alarm周期性的触发每隔五秒产生信号SIGALRM,然后通过管道让主函数去处理定时器链表上的定时任务------关闭非活动连接。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "lst_timer.h"
#define FD_LIMIT 65535
#define MAX_EVENT_NUMBER 1024
#define TIMESLOT 5
static int pipefd[2];
static sort_timer_lst timer_lst;
static int epollfd = 0;
/* 将套接字设置为非阻塞 */
int setnonblocking( int fd )
{
int old_option = fcntl( fd, F_GETFL );
int new_option = old_option | O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl( fd, F_SETFL, new_option );
return old_option;
}
/*添加套接字*/
void addfd( int epollfd, int fd )
{
epoll_event event;
event.data.fd = fd;
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
epoll_ctl( epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &event );
setnonblocking( fd );
}
/*信号处理函数*/
void sig_handler( int sig )
{
int save_errno = errno;
int msg = sig;
/*将信号量值写到写段*/
send( pipefd[1], ( char* )&msg, 1, 0 );
errno = save_errno;
}
/*添加信号*/
void addsig( int sig )
{
struct sigaction sa;
memset( &sa, '\0', sizeof( sa ) );
/*函数指针赋值*/
sa.sa_handler = sig_handler;
sa.sa_flags |= SA_RESTART;
sigfillset( &sa.sa_mask );
assert( sigaction( sig, &sa, NULL ) != -1 );
}
void timer_handler()
{
timer_lst.tick();
alarm( TIMESLOT );
}
/*定时器回调函数 会将套接字删除掉*/
void cb_func( client_data* user_data )
{
epoll_ctl( epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, user_data->sockfd, 0 );
assert( user_data );
close( user_data->sockfd );
printf( "close fd %d\n", user_data->sockfd );
}
int main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{
if( argc <= 2 )
{
printf( "usage: %s ip_address port_number\n", basename( argv[0] ) );
return 1;
}
const char* ip = argv[1];
int port = atoi( argv[2] );
int ret = 0;
struct sockaddr_in address;
bzero( &address, sizeof( address ) );
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton( AF_INET, ip, &address.sin_addr );
address.sin_port = htons( port );
int listenfd = socket( PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 );
assert( listenfd >= 0 );
ret = bind( listenfd, ( struct sockaddr* )&address, sizeof( address ) );
assert( ret != -1 );
ret = listen( listenfd, 5 );
assert( ret != -1 );
epoll_event events[ MAX_EVENT_NUMBER ];
int epollfd = epoll_create( 5 );
assert( epollfd != -1 );
addfd( epollfd, listenfd );
/* 这个还是统一事件源的思路 创建了一罐接收并处理信号的管道 */
ret = socketpair( PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, pipefd );
assert( ret != -1 );
setnonblocking( pipefd[1] );
addfd( epollfd, pipefd[0] );
// add all the interesting signals here
addsig( SIGALRM );
addsig( SIGTERM );
bool stop_server = false;
client_data* users = new client_data[FD_LIMIT];
bool timeout = false;
/*
* alarm也称为闹钟函数,它可以在进程中设置一个定时器,当定时器指定的时间到时,
* 它向进程发送SIGALRM信号。可以设置忽略或者不捕获此信号,
* 如果采用默认方式其动作是终止调用该alarm函数的进程。
* 一个进程只能有一个 指定5秒
* 不可重入
*/
alarm( TIMESLOT );
while( !stop_server )
{
int number = epoll_wait( epollfd, events, MAX_EVENT_NUMBER, -1 );
if ( ( number < 0 ) && ( errno != EINTR ) )
{
printf( "epoll failure\n" );
break;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < number; i++ )
{
int sockfd = events[i].data.fd;
/* 处理连接请求 */
if( sockfd == listenfd )
{
struct sockaddr_in client_address;
socklen_t client_addrlength = sizeof( client_address );
int connfd = accept( listenfd, ( struct sockaddr* )&client_address, &client_addrlength );
addfd( epollfd, connfd );
users[connfd].address = client_address;
users[connfd].sockfd = connfd;
util_timer* timer = new util_timer;
timer->user_data = &users[connfd];
timer->cb_func = cb_func;
time_t cur = time( NULL );
timer->expire = cur + 3 * TIMESLOT;
users[connfd].timer = timer;
timer_lst.add_timer( timer );
}
/* 是从信号管道来的消息 并且可读 */
else if( ( sockfd == pipefd[0] ) && ( events[i].events & EPOLLIN ) )
{
int sig;
char signals[1024];
ret = recv( pipefd[0], signals, sizeof( signals ), 0 );
if( ret == -1 )
{
// handle the error
continue;
}
else if( ret == 0 )
{
continue;
}
else
{
for( int i = 0; i < ret; ++i )
{
switch( signals[i] )
{
case SIGALRM:
{
/*这个是系统定时任务 放到最后处理 也就是说在五秒种之内
* 服务器没什么变化就信号产生*/
printf("五秒到辣\n");
timeout = true;
break;
}
case SIGTERM:
{
printf("听说有人想让我退出\n");
stop_server = true;
}
}
}
}
}
/* 从客户端收到消息 */
else if( events[i].events & EPOLLIN )
{
memset( users[sockfd].buf, '\0', BUFFER_SIZE );
ret = recv( sockfd, users[sockfd].buf, BUFFER_SIZE-1, 0 );
printf( "get %d bytes of client data %s from %d\n", ret, users[sockfd].buf, sockfd );
util_timer* timer = users[sockfd].timer;
if( ret < 0 )
{
if( errno != EAGAIN )
{
cb_func( &users[sockfd] );
if( timer )
{
timer_lst.del_timer( timer );
}
}
}
else if( ret == 0 )
{
cb_func( &users[sockfd] );
if( timer )
{
timer_lst.del_timer( timer );
}
}
else
{
// send( sockfd, users[sockfd].buf, BUFFER_SIZE-1, 0 );
/* 客户端有数据 此为活动链接 所有延迟此客户端的被关闭时间 */
if( timer )
{
time_t cur = time( NULL );
timer->expire = cur + 3 * TIMESLOT;
printf( "adjust timer once\n" );
timer_lst.adjust_timer( timer );
}
}
}
else
{
// others
}
}
if( timeout )
{
timer_handler();
timeout = false;
}
}
close( listenfd );
close( pipefd[1] );
close( pipefd[0] );
delete [] users;
return 0;
}
编译: g++ timer_list.cc -o timer_list -pthread
运行: ./timer_list localhost 8888 //(在本地测)
客户端连接就用: telnet localhost 8888
编译运行好之后 发现是不是道理很简单啊,一直while循环遍历链表查看是否有到期事件就ok了嘛。
好这里给之后的高性能定时器做了一个铺垫。
`
经过这样一个流程下来,是不是惊呼“不过如此”!
让我们再看一下开篇的这句话!
我们通常所说的定时器是定时器容器,是容器类数据结构。
定时器是容器内容纳的一个对象,是对定时器的封装。
添加定时器复杂度为O(n)
删除定时器复杂度为O(1)
执行定时任务的复杂度为O(1)
看起来数据还不错,但是这个思路这个其实相当于一个心跳函数,每隔一段时间调用一次,当某一段时间没有任务也调用它是不是就会浪费资源呀,所以我们在之后两节的目的就是寻找更加高效的数据结构和算法来处理定时器任务。
后续内容 敬请期待