跳跃列表是一种数据结构。他允许快速查询一个有序连续元素的数据链表。平均查找和插入的事件复杂度为O(log(n)),优于普通链表O(n)。快速查询是通过维护一个多层次的链表,并且每一层链表中的元素是前一层链表元素的子集。
具体描述:

在levelDb中跳跃列表每个节点的数据结构如下所示:
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) {}
Key const key;
// Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return next_[n].load(std::memory_order_acquire);
}
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].store(x, std::memory_order_release);
}
// No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return next_[n].load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].store(x, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
std::atomic<Node*> next_[1];
};
可以看出 std::atomic<Node*> next_[1]成员就可以构建跳表的层数。
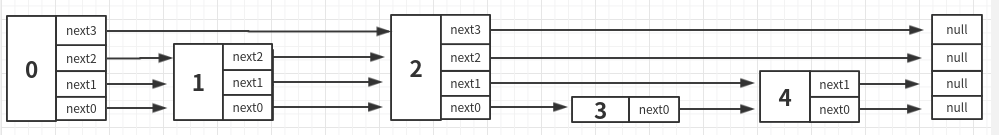
其中层数是一个随机数。
跳跃列表不像平衡树等数据结构那样提供对最坏情况的性能保证:由于用来建造跳跃列表采用随机选取元素进入更高层
的方法,在小概率情况下会生成一个不平衡的跳跃列表(最坏情况例如最底层仅有一个元素进入了更高层,此时跳跃列
表的查找与普通列表一致)。但是在实际中它通常工作良好,随机化平衡方案也比平衡二叉查找树等数据结构中使用的
确定性平衡方案容易实现。跳跃列表在并行计算中也很有用:插入可以在跳跃列表不同的部分并行地进行,而不用对数
据结构进行全局的重新平衡。
实现细节:
因为跳跃列表中的元素可以在多个列表中,所以每个元素可以有多于一个指针。跳跃列表的插入和删除的实现与普通的链表操作类似,但高层元素必须在进行多个链表中进行插入或删除。
跳跃列表的最坏时间性能具有一定随机性,但是可以通过时间复杂度为 O(n)的遍历操作(例如在打印列表全部内容时)以无随机的算法重整列表的结构,从而使跳跃列表的实际查找时间复杂度尽量符合理论平均值 O(log(n))。
插入操作:
先定义 记录已经遍历的节点的指针数组,开始找好合适的位置进行插入操作。即调用FindGreaterOrEqual。
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
//记录插入节点插入位置的前一个节点
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
//找合适的插入位置
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == nullptr || !Equal(key, x->key));
//跟要插入节点确定一个层高
int height = RandomHeight();
//比当前最高层要高
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
//将最高层记录指向head_
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (nullptr), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since nullptr sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
max_height_.store(height, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
//创建新的节点,这里使用内存池根据传入的层高给新节点分配空间
//并将相应的键值设置好
x = NewNode(key, height);
//相链表插入新的节点一样插入,这里从底层开始,指向下一个节点的对应层次上
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
//在链表中找合适的插入点
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key,
Node** prev) const {
//先记录跳跃表的头指针
Node* x = head_;
//获取跳跃表的层数
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
//从较高节点处开始,遍历跳跃表
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
//将当前节点键值和插入的键值进行比较
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
//不符合条件继续找
x = next;
}
//找到了
else {
//找到了,通过prev指针数组将节点记录下来
if (prev != nullptr) prev[level] = x;
//将当前节点leve减为0的时候将next返回
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
}
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key, Comparator>::KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const {
// null n is considered infinite
//节点不为空,将当前键值和插入键值进行比较
return (n != nullptr) && (compare_(n->key, key) < 0);
}
自己实现的跳表,使用智能指针,无需考虑内存释放问题:
skipList.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <memory>
#define TYPE template <typename keyType, typename valType>
#define CLASS Node<keyType, valType>
#define SKIPCLASS skipList<keyType, valType>
using namespace std ;
//使用leveldb中的随机数生成器
class Random {
private:
uint32_t seed_;
public:
explicit Random(uint32_t s) : seed_(s & 0x7fffffffu) {
// Avoid bad seeds.
if (seed_ == 0 || seed_ == 2147483647L) {
seed_ = 1;
}
}
uint32_t Next() {
static const uint32_t M = 2147483647L; // 2^31-1
static const uint64_t A = 16807; // bits 14, 8, 7, 5, 2, 1, 0
uint64_t product = seed_ * A;
seed_ = static_cast<uint32_t>((product >> 31) + (product & M));
if (seed_ > M) {
seed_ -= M;
}
return seed_;
}
uint32_t Uniform(int n) { return (Next() % n); }
bool OneIn(int n) { return (Next() % n) == 0; }
uint32_t Skewed(int max_log) {
return Uniform(1 << Uniform(max_log + 1));
}
};
TYPE
class Node {
public :
Node() {}
~Node() {}
public :
keyType key ;
valType value ;
//后继指针数组
vector<shared_ptr<CLASS>>next ;
};
TYPE
class skipList {
public:
skipList():level(1), head(nullptr), rnd(0xdeadbeef) {}
~skipList() {}
shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS> createSkipList() ;
shared_ptr<CLASS> createNode(int level, keyType key, valType val) ;
bool insert(shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS>sl, keyType key, valType val) ;
valType* search(shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS>sl, keyType key) ;
bool erase(shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS>sl, keyType key) ;
int getLevel() ;
public :
int level ; //层数
shared_ptr<CLASS> head ;
//最大层数
Random rnd ;
};
//随机产生当前跳表的层数
TYPE
int SKIPCLASS :: getLevel() {
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
while (height < level && ((rnd.Next() % kBranching) == 0)) {
height++;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= level);
return height;
}
//创建一个新的跳表节点
TYPE
shared_ptr<CLASS> SKIPCLASS :: createNode(int level, keyType key, valType val) {
//创建节点
shared_ptr<CLASS> p = make_shared<CLASS>() ;
//跳表的层空间
p->next.reserve(level) ;
//申请层数
//设置键值
p->key = key ;
p->value = val ;
return p ;
}
//创建跳表
TYPE
shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS> SKIPCLASS :: createSkipList() {
//创建新的跳表
shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS> sl = make_shared<SKIPCLASS>() ;
//预设跳表层数为0
//创建跳表节点
int level = getLevel() ;
//设置高度
sl->level = level ;
shared_ptr<CLASS> h = createNode(level, 0, 0) ;
sl -> head = h ;
//将head的next数组清空
for(int i=0; i<level; i++) {
h->next[i] = nullptr ;
}
srand(time(0)) ;
return sl ;
}
//跳表的插入操作
TYPE
bool SKIPCLASS :: insert(shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS>sl, keyType key, valType val) {
cout << "插入元素:" << endl ;
vector<shared_ptr<CLASS>>update ;
update.reserve(level) ;
shared_ptr<CLASS> q, p = sl->head ;
//从最高层开始,进行搜索
int i=sl->level-1;
for(;i>=0;i--) {
//q->next[i]不为空并且p->next[i]中的key小于插入的key
while((q=p->next[i])&&q->key<key) {
p=q ;
}
//找打了插入点的前一个节点保存
update[i] = p ;
}
//key等于插入的key,只修改相应的值
if(q && q->key == key) {
q->value = val ;
return true ;
}
int level = getLevel() ;
//产生的随机数比跳表的层数大,则在update中将新添加的层指向header
if(level > sl->level) {
//扩增update
update.reserve(level) ;
//使得插入点的前一个节点保存头结点,头结点在跳跃表中的level应该是最高的
for(int i=sl->level; i<level; i++) {
update[i] = sl->head ;
}
//设置跳表的层数为level
sl->level = level ;
}
//创建一个节点
q = createNode(level, key, val) ;
//新建一个待插入节点,前一个节点一层层插入
for(int i=level-1; i>=0; --i) {
q->next[i] = update[i]->next[i] ;
update[i]->next[i] = q ;
}
cout << "插入元素成功~!" << endl ;
return true ;
}
//调表删除节点操作
TYPE
bool SKIPCLASS :: erase(shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS> sl, keyType key) {
vector<shared_ptr<CLASS>> update ;
shared_ptr<CLASS>q = nullptr, p = sl->head ;
update.reserve(level) ;
int i = sl->level -1 ;
for(; i>=0; --i) {
while((q = p->next[i]) && q->key < key) {
p = q ;
}
update[i] = p ;
}
//判断是否为待删除的键
if(!q || (q&&q->key != key)) {
return false ;
}
//逐层删除
for(i=sl->level-1; i>=0; --i) {
if(update[i]->next[i] == q) {
update[i]->next[i] = q->next[i] ;
}
if(sl->head->next[i] == nullptr) {
sl->level -- ;
}
}
q = nullptr ;
return true ;
}
//跳表的查找
TYPE
valType* SKIPCLASS :: search(shared_ptr<SKIPCLASS>sl, keyType key) {
shared_ptr<CLASS> q, p = sl->head ;
q = nullptr ;
int i = sl->level-1 ;
for(; i>=0; --i) {
while((q = p->next[i]) && q->key < key) {
p = q ;
}
if(q && (key == q->key)) {
return &q->value ;
}
}
return nullptr ;
}
test.cpp
#include "skipList.h"
int main() {
shared_ptr<skipList<int, int>> sl = make_shared<skipList<int, int>>() ;
//创建skiplist
sl = sl->createSkipList() ;
sl->insert(sl, 1, 1) ;
sl->insert(sl, 2, 3) ;
sl->insert(sl, 5, 3) ;
sl->insert(sl, 7, 3) ;
sl->insert(sl, 9, 3) ;
sl->insert(sl, 10, 3) ;
cout << "获取键为1的值:"<< *sl->search(sl, 1) << endl ;
cout << "获取键为2的值:" << *sl->search(sl, 2) << endl ;
cout << "删除键为:1" << " 删除结果"<< sl->erase(sl, 1) << endl ;
cout << "找键为1的值-------->" << endl ;
if(sl->search(sl, 1) == nullptr) {
cout << "没找到节点" << endl ;
return 1 ;
} else
cout << "找到了节点!" << endl ;
}
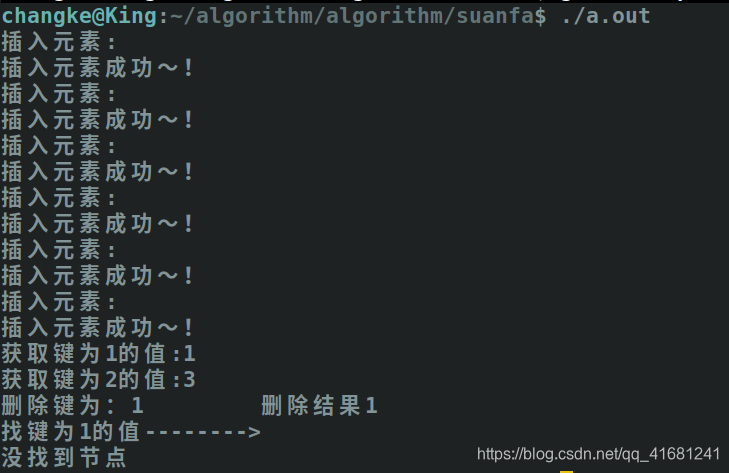
运行结果: