目录
定义节点
一个简单的节点只包括数据和指向下一个节点的指针
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node*next;
};
创建链表
定义一个结构体类型的头指针,之后将通过这个指针来访问链表这里把它写成一个函数
struct Node* createlist()
{
struct Node *head;
head=NULL;
return head;
}
头插法插入节点
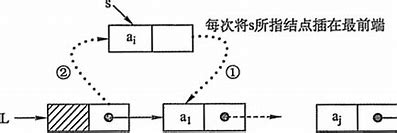
每次将新节点插在头指针后面,再让新节点指向原来的节点
void insert(struct Node **head,int a)
{
struct Node *temp=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->next=NULL;
temp->data=a;
if (*head==NULL)//需要判断链表是否为空
{
*head=temp;//若为空,则让头指针直接指向新节点
}
else
{ //不为空则让新节点指向头指针后的一个节点,再让头指针指向他
temp->next=*head;
*head=temp;
}
}
这里用到了二级指针,若要在函数中修改指针的值,就要使用指向指针的指针,注意实际参数应传入&list链表头指针的地址。若不需要修改头指针则可只用一级指针
尾插法
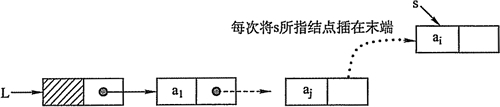
第一种方法:
遍历链表找出尾节点,再向新节点插在它后面。这种方法每次都要遍历一遍链表,容易理解但比较麻烦。
下面给出代码:
void weicha(struct Node **head,int a) //每次都要找尾节点
{
struct Node *temp=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node*p=*head;
temp->next=NULL;
temp->data=a;
if (*head==NULL)//和头插法一样需要判断链表是否为空
{
*head=temp;
}
else
{
while(p->next!=NULL)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next=temp;
}
}
下面给出较为简单的第二种方法:
定义一个尾指针,让它一直指向链表尾部。这样每次都可以直接插入。
void weicha1(struct Node **head,int a) //定义tail一直指向尾
{
struct Node *temp=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
static struct Node*tail;
struct Node*p=*head;
temp->next=NULL;
temp->data=a;
if (*head==NULL)//若链表为空,则插入的第一个节点既是头节点又是尾节点。
{
*head=temp;
tail=temp;
}
else
{
tail->next=temp;
}
tail=temp;//插入后新节点将变成尾节点
}
这里需将尾指针定义为静态变量,这样尾指针可以一直存在。
遍历输出
定义一个临时变量p让它从头节点遍历到尾部。
void display(struct Node*head)
{
struct Node*p=head;
if (p==NULL)
printf("链表为空");
while (p!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\n",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
删除整表
删除节点后用free()函数释放空间
void deletelist(struct Node**head)
{
struct Node *p;
while (*head!=NULL)
{
p=*head;
*head=(*head)->next;
free(p);
}
}
查找元素(返回节点指针)
struct Node *searchnode(struct Node *head,int a)
{
struct Node *p;
p=head;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if (p->data==a)
{
break;
}
p=p->next;
}
return p;
}
完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node*next;
};
struct Node* createlist()
{
struct Node *head;
head=NULL;
return head;
}
void insert(struct Node **head,int a)
{
struct Node *temp=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->next=NULL;
temp->data=a;
if (*head==NULL)
{
*head=temp;
}
else
{
temp->next=*head;
*head=temp;
}
}
void weicha(struct Node **head,int a) //每次都要找
{
struct Node *temp=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node*p=*head;
temp->next=NULL;
temp->data=a;
if (*head==NULL)
{
*head=temp;
}
else
{
while(p->next!=NULL)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next=temp;
}
}
void weicha1(struct Node **head,int a) //定义tail一直指向尾
{
struct Node *temp=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
static struct Node*tail;
struct Node*p=*head;
temp->next=NULL;
temp->data=a;
if (*head==NULL)
{
*head=temp;
tail=temp;
}
else
{
tail->next=temp;
}
tail=temp;
}
void display(struct Node*head)
{
struct Node*p=head;
if (p==NULL)
printf("emmm");
while (p!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\n",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
void deletelist(struct Node**head)
{
struct Node *p;
while (*head!=NULL)
{
p=*head;
*head=(*head)->next;
free(p);
}
}
struct Node *searchnode(struct Node *head,int a)
{
struct Node *p;
p=head;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if (p->data==a)
{
break;
}
p=p->next;
}
return p;
}
int main()
{
struct Node* ban=createlist();
weicha1(&ban,1);
weicha1(&ban,2);
weicha1(&ban,3);
weicha1(&ban,4);
display(ban);
struct Node *a=searchnode(ban,3);
a->data=4;
display(ban);
}