There are literally dozens of snooker competitions held each year, and team Jinotega tries to attend them all (for some reason they prefer name "snookah")! When a competition takes place somewhere far from their hometown, Ivan, Artsem and Konstantin take a flight to the contest and back.
Jinotega's best friends, team Base have found a list of their itinerary receipts with information about departure and arrival airports. Now they wonder, where is Jinotega now: at home or at some competition far away? They know that:
- this list contains all Jinotega's flights in this year (in arbitrary order),
- Jinotega has only flown from his hometown to a snooker contest and back,
- after each competition Jinotega flies back home (though they may attend a competition in one place several times),
- and finally, at the beginning of the year Jinotega was at home.
Please help them to determine Jinotega's location!
In the first line of input there is a single integer n: the number of Jinotega's flights (1 ≤ n ≤ 100). In the second line there is a string of 3capital Latin letters: the name of Jinotega's home airport. In the next n lines there is flight information, one flight per line, in form "XXX->YYY", where "XXX" is the name of departure airport "YYY" is the name of arrival airport. Exactly one of these airports is Jinotega's home airport.
It is guaranteed that flights information is consistent with the knowledge of Jinotega's friends, which is described in the main part of the statement.
If Jinotega is now at home, print "home" (without quotes), otherwise print "contest".
4 SVO SVO->CDG LHR->SVO SVO->LHR CDG->SVO
home
3 SVO SVO->HKT HKT->SVO SVO->RAP
contest
In the first sample Jinotega might first fly from SVO to CDG and back, and then from SVO to LHR and back, so now they should be at home. In the second sample Jinotega must now be at RAP because a flight from RAP back to SVO is not on the list.
解题思路:
直接统计一边其回家的次数和离开家的次数,是否相等。
想等则在家,否则在外面。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define rep(i,m,n) for(int i=m;i<=n;i++)
#define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
const int inf_int = 2e9;
const long long inf_ll = 2e18;
#define inf_add 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pb push_back
//#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define Lson L, mid, rt<<1
#define Rson mid+1, R, rt<<1|1
const int maxn=5e2+10;
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> vi;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline int read(){int ra,fh;char rx;rx=getchar(),ra=0,fh=1;
while((rx<'0'||rx>'9')&&rx!='-')rx=getchar();if(rx=='-')
fh=-1,rx=getchar();while(rx>='0'&&rx<='9')ra*=10,ra+=rx-48,
rx=getchar();return ra*fh;}
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;}
int dir[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
const int N = 1e5+5;
typedef struct node{
int x;
int y;
}NODE;
int n,k;
string home,t;
vi re;
vector<string> c;
map<string,int> ss;
map<string,int>::iterator it;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
cin >> home;
rep(i,0,n-1)
{
cin >> t;
c.push_back(t);
t.clear();
t+=c[i][0];
t+=c[i][1];
t+=c[i][2];
if(!ss[t])
ss[t]=110;
ss[t]++;
t.clear();
t+=c[i][5];
t+=c[i][6];
t+=c[i][7];
if(!ss[t])
ss[t]=110;
ss[t]--;
}
for(it=ss.begin();it!=ss.end();it++)
{
if((it->second)!=110)
{
cout << "contest"<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "home"<<endl;
return 0;
}
解题思路:
按照其规则进行模拟,看是否符合条件,
坑点:第一个一定为a
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define rep(i,m,n) for(int i=m;i<=n;i++)
#define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
const int inf_int = 2e9;
const long long inf_ll = 2e18;
#define inf_add 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pb push_back
//#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define Lson L, mid, rt<<1
#define Rson mid+1, R, rt<<1|1
const int maxn=5e2+10;
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> vi;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline int read(){int ra,fh;char rx;rx=getchar(),ra=0,fh=1;
while((rx<'0'||rx>'9')&&rx!='-')rx=getchar();if(rx=='-')
fh=-1,rx=getchar();while(rx>='0'&&rx<='9')ra*=10,ra+=rx-48,
rx=getchar();return ra*fh;}
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;}
int dir[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
const int N = 1e5+5;
typedef struct node{
int x;
int y;
}NODE;
int n,k;
string s;
vi re;
int flag[100];
int main()
{
cin >>s;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
{
if(flag[s[i]-'a']==0)
{
re.push_back(s[i]-'a');
flag[s[i]-'a']++;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
if(re[0]!=0)
{
cout << "NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<re.size()-1;i++)
{
if(re[i]!=re[i+1]-1)
{
cout << "NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "YES"<<endl;
return 0;
}
解题思路:
根据其所给的函数特性,可知,其需要满足以下条件:
如果多个数对应一个数f[i] ,则在这多个数当中必须有一个数等于f[i]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define rep(i,m,n) for(int i=m;i<=n;i++)
#define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
const int inf_int = 2e9;
const long long inf_ll = 2e18;
#define inf_add 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pb push_back
//#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define Lson L, mid, rt<<1
#define Rson mid+1, R, rt<<1|1
const int maxn=5e2+10;
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> vi;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline int read(){int ra,fh;char rx;rx=getchar(),ra=0,fh=1;
while((rx<'0'||rx>'9')&&rx!='-')rx=getchar();if(rx=='-')
fh=-1,rx=getchar();while(rx>='0'&&rx<='9')ra*=10,ra+=rx-48,
rx=getchar();return ra*fh;}
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;}
int dir[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
const int N = 1e6+5;
typedef struct node{
int x;
int index;
}NODE;
bool cmp(NODE x,NODE y)
{
return x.x<y.x;
}
vector<NODE> a;
vi aa;
ll n ,m;
ll f[N];
ll g[N],h[N];
int main()
{
NODE t;
cin>>n;
rep(i,1,n)
{
cin >> f[i];
t.x = f[i];
t.index = i;
a.push_back(t);
}
//make the same value together
sort(a.begin(),a.end(),cmp);
NODE tt;
tt.x = 0;
tt.index =0;
int i=0;
while(1)
{
if(i>=n) break;
int t1 = i;
while(a[i].x==a[i+1].x&&i<n-1) i++;
aa.push_back(a[i].x);
int len = aa.size();
int flag = -1;
for(int j=t1;j<=i;j++)
{
if(a[j].x==a[j].index)
{
flag = j;
break;
}
}
if(flag==-1)
{
cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
for(int j=t1;j<=i;j++)
{
g[a[j].index] = len;
}
h[len] = a[flag].x;
i++;
}
cout << aa.size()<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cout << g[i]<<" ";
}
cout <<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=aa.size();i++)
{
cout << h[i]<<" ";
}
cout <<endl;
return 0;
}
Vanya wants to minimize a tree. He can perform the following operation multiple times: choose a vertex v, and two disjoint (except for v) paths of equal length a0 = v, a1, ..., ak, and b0 = v, b1, ..., bk. Additionally, vertices a1, ..., ak, b1, ..., bk must not have any neighbours in the tree other than adjacent vertices of corresponding paths. After that, one of the paths may be merged into the other, that is, the vertices b1, ..., bk can be effectively erased:
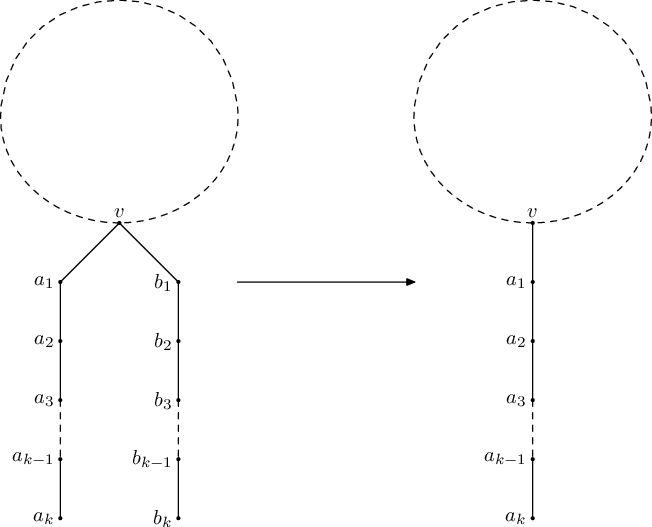
Help Vanya determine if it possible to make the tree into a path via a sequence of described operations, and if the answer is positive, also determine the shortest length of such path.
The first line of input contains the number of vertices n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105).
Next n - 1 lines describe edges of the tree. Each of these lines contains two space-separated integers u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v) — indices of endpoints of the corresponding edge. It is guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
If it is impossible to obtain a path, print -1. Otherwise, print the minimum number of edges in a possible path.
6 1 2 2 3 2 4 4 5 1 6
3
7 1 2 1 3 3 4 1 5 5 6 6 7
-1
In the first sample case, a path of three edges is obtained after merging paths 2 - 1 - 6 and 2 - 4 - 5.
It is impossible to perform any operation in the second sample case. For example, it is impossible to merge paths 1 - 3 - 4 and 1 - 5 - 6, since vertex 6 additionally has a neighbour 7 that is not present in the corresponding path.
解题思路:
进行模拟,从叶子节点开始,沿单一路径走,边走边删,并用一个数组记录每个节点到叶子节点的长度
如果最后剩一个节点且其有1或两条路径到达叶子节点,则可达
否则,其无法删成一条路径。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define rep(i,m,n) for(int i=m;i<=n;i++)
#define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
const int inf_int = 2e9;
const long long inf_ll = 2e18;
#define inf_add 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pb push_back
//#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define Lson L, mid, rt<<1
#define Rson mid+1, R, rt<<1|1
const int maxn=5e2+10;
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> vi;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline int read(){int ra,fh;char rx;rx=getchar(),ra=0,fh=1;
while((rx<'0'||rx>'9')&&rx!='-')rx=getchar();if(rx=='-')
fh=-1,rx=getchar();while(rx>='0'&&rx<='9')ra*=10,ra+=rx-48,
rx=getchar();return ra*fh;}
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;}
int dir[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
const int N = 1e5+5;
typedef struct node{
int x;
int index;
}NODE;
int bfs();
int vis[N*2];
set<int> mpp[N*2];
set<int> ct[N*2];
vi one;
int du[N*2];
int u,v;
int n;
int main()
{
cin >>n;
rep(i,1,n-1)
{
cin >> u>>v;
mpp[u].insert(v);
mpp[v].insert(u);
du[u]++,du[v]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(du[i]==1)
{
one.push_back(i);
}
}
cout << bfs()<<endl;
return 0;
}
int bfs()
{
queue<int> q;
for(auto &r:one)
{
q.push(r);
ct[r].insert(0);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(vis[cur])
continue;
if(mpp[cur].size()==1)
{
if(ct[cur].size()==1)
{
int nex = *mpp[cur].begin();
mpp[cur].clear();
int len = mpp[nex].size();
mpp[nex].erase(cur);
ct[nex].insert(*ct[cur].begin()+1);
q.push(nex);
vis[cur]=1;
}
}
else if(mpp[cur].empty())
{
//cout <<cur<<endl;
//cout << ct[cur].size()<<endl;
if(ct[cur].size()>2)
{
return -1;
}
else if(ct[cur].size()==1)
{
int t =*ct[cur].begin();
while(t%2==0)
t/=2;
return t;
}
else
{
int t = *ct[cur].begin()+ *ct[cur].rbegin();
while(t%2==0)
t/=2;
return t;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
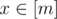 , and
, and  , or determine that finding these is impossible.
, or determine that finding these is impossible.